以太坊的工作原理是什么?不管你们知不知道以太坊(Ethereum blockchain)是什么,但是你们大概都听说过以太坊。最近在新闻里出现过很多次,包括一些专业杂志的封面,但是如果你们对以太坊到底是什么没有一个基本的了解的话,看这些文章就会感觉跟看天书一样。
What is Etherm’s working principle? Whether you know or not what Etherium blockchain is, you've probably heard of it. There have been many times in the news recently, including the cover of some professional magazines, but if you don’t have a basic idea of what Ether is, reading these articles will feel like reading the Book.
所以,什么是以太坊?本质上,就是一个保存数字交易永久记录的公共数据库。重要的是,这个数据库不需要任何中央权威机构来维持和保护它。相反的它以一个“无信任”的交易系统来运行一个个体在不需要信任任何第三方或对方的情况下进行点对点交易的架构。
So, what's in Tai Chamber? In essence, it's a public database that keeps permanent records of digital transactions. What's important is that this database does not require any central authority to maintain and protect it. Instead, it runs an “untrusted” trading system in which individuals conduct point-to-point transactions without having to trust any third party or each other.

依然感到很困惑?这就是这篇文章存在的理由。我的目标是在技术层面来解释以太坊的工作原理,但是不会出现很复杂的数学问题或看起来很可怕的公式。即使你不是一个程序员,我希望你看完之后最起码对技术有个更好的认识。如果有些部分技术性太强不好理解,这是非常正常的,真的没有必要完全理解每一个小细节。我建议只要宏观的理解一下事物就行了。
That's why this article exists. My goal is to explain at the technical level the principles of Etherm, but there will be no very complex mathematical problems or seemingly terrible formulas. Even if you are not a programmer, I hope that you will at least have a better understanding of technology. If some are too technical to understand, it's perfectly normal, and there is really no need to fully understand every little detail. I suggest that just a macro understanding of things.
这篇文章中的很多议点都是以太坊黄皮书中讨论过的概念的细分。我添加了我自己的解释和图表使理解以太坊更加简单一点。那些足够勇敢的人可以挑战一下技术,去阅读一下以太坊的黄皮书。
Many of the points in this article are broken down by the concepts discussed in Taiwan’s yellow book. I added my own explanations and graphs to make it easier to understand it. Those brave enough to challenge technology to read it.
好了, 让我们开始吧!
All right, let's do it!
区块链定义
Block Chain Definition
区块链就是一个具有共享状态的密码性安全交易的单机(cryptographically secure transactional singleton machine with shared-state)。[1]这有点长,是吧?让我们将它分开来看:
The block chain is a single machine with a secret security transaction in a shared state.[1] It's a little long, isn't it? Let's separate it:
“密码性安全(Cryptographically secure)”是指用一个很难被解开的复杂数学机制算法来保证数字货币生产的安全性。将它想象成类似于防火墙的这种。它们使得欺骗系统近乎是一个不可能的事情(比如:构造一笔假的交易,消除一笔交易等等)。
"Cryptopographically secure" means using a complex mathematical mechanism algorithm that is difficult to unshape to ensure the safety of digital money production. Imagine it as a firewall. They make it almost impossible to deceive the system (e.g. to construct a fake transaction, eliminate a transaction, etc.).
“交易的单机(Transactional singleton machine)”是指只有一个权威的机器实例为系统中产生的交易负责任。换句话说,只有一个全球真相是大家所相信的。
“Transactional transaction machine” means that there is only one authoritative example of machinery responsible for the transactions generated in the system. In other words, there is only one global truth that you believe.
“具有共享状态(With shared-state)”是指在这台机器上存储的状态是共享的,对每个人都是开放的。
“With shared-state” means that the state stored on this machine is shared and open to everyone.
以太坊实现了区块链的这个范例。
This example of the block chain has been made possible by Ether.
以太坊模型说明
The Etherkom model says:
以太坊的本质就是一个基于交易的状态机(transaction-based state machine)。在计算机科学中,一个 状态机 是指可以读取一系列的输入,然后根据这些输入,会转换成一个新的状态出来的东西。
The essence of Ether is a trading-based state machine. In computer science, a state machine is something that can read a series of inputs and then, based on them, converts to a new state.
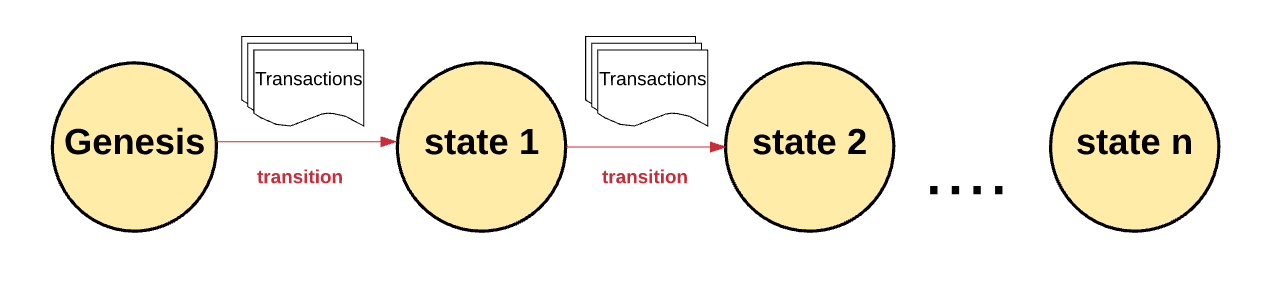
根据以太坊的状态机,我们从创世纪状态(genesis state)开始。这差不多类似于一片空白的石板,在网络中还没有任何交易的产生状态。当交易被执行后,这个创世纪状态就会转变成最终状态。在任何时刻,这个最终状态都代表着以太坊当前的状态。
According to the Etheria state machine, we start with the Genesis state. It's kind of like a blank tablet, and there's no deal in the network. When the deal is implemented, the Genesis state becomes the final state. At any moment, this final state represents the current state of the Ether chamber.
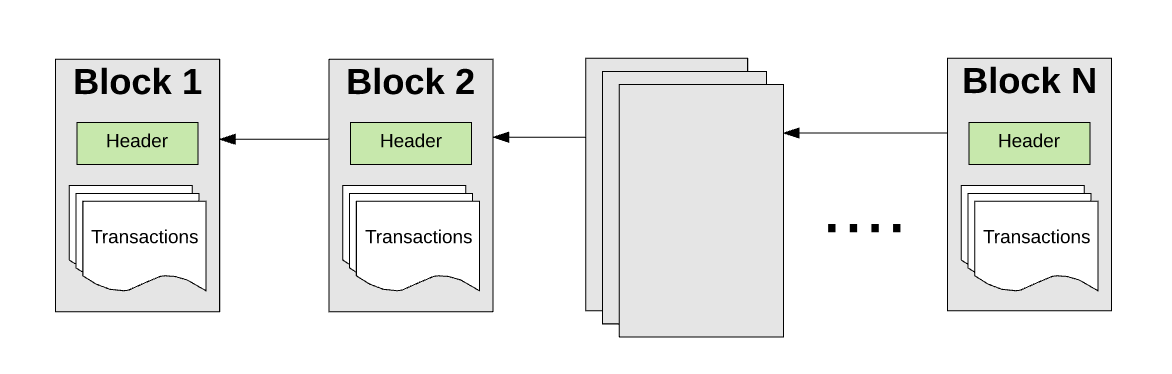
以太坊的状态有百万个交易。这些交易都被“组团”到一个区块中。一个区块包含了一系列的交易,每个区块都与它的前一个区块链接起来。
There are millions of transactions in Etheria's state. All of these transactions are "grouped" into a block. One block contains a series of transactions, each linked to its previous block.
为了让一个状态转换成下一个状态,交易必须是有效的。为了让一个交易被认为是有效的,它必须要经过一个验证过程,此过程也就是挖矿。挖矿就是一组节点(即电脑)用它们的计算资源来创建一个包含有效交易的区块出来。
In order for a state to be converted to the next state, the transaction must be valid. In order for a transaction to be considered valid, it has to go through a validation process, which is mining. Mining is a set of nodes (i.e. computers) that use their computing resources to create a block containing a valid transaction.
任何在网络上宣称自己是矿工的节点都可以尝试创建和验证区块。世界各地的很多矿工都在同一时间创建和验证区块。每个矿工在提交一个区块到区块链上的时候都会提供一个数学机制的“证明”,这个证明就像一个保证:如果这个证明存在,那么这个区块一定是有效的。
Any node that claims to be a miner on the web can try to create and validate blocks. Many miners around the world create and authenticate blocks at the same time. Each miner, when submitting a block to the chain of blocks, provides a mathematical “procedure” that is like a guarantee that, if it exists, the block must be valid.
为了让一个区块添加到主链上,一个矿工必须要比其他矿工更快的提供出这个“证明”。通过矿工提供的一个数学机制的“证明”来证实每个区块的过程称之为工作量证明(proof of work)。
In order for a block to be added to the main chain, a miner must provide this “evidence” faster than any other miner. The process of each block is referred to as the workload certificate (proof of work) by means of a “evidence” from a mathematical mechanism provided by the miner.
证实了一个新区块的矿工都会被奖励一定价值的奖赏。奖赏是什么?以太坊使用一种内在数字代币-以太币(Ether)作为奖赏。每次矿工证明了一个新区块,那么就会产生一个新的以太币并被奖励给矿工。
The miners who confirm a new block will be rewarded with a certain value. What is the reward? The community uses an inner digital token as a reward. Every time the miners prove a new block, a new Ether will be created and rewarded to the miners.
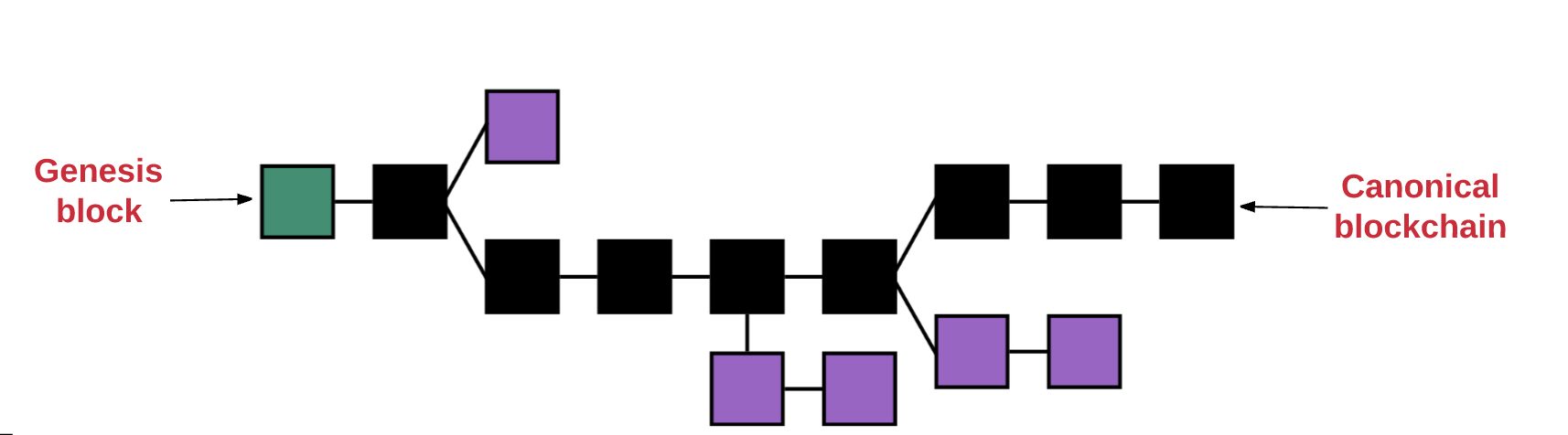
你也许会在想:什么能确保每个人都只在区块的同一条链上呢?我们怎么能确定不会存在一部分矿工创建一个他们自己的链呢?
And you may wonder: What will ensure that everyone is only on the same chain of blocks? How can we be sure that there will not be a portion of the miners who create a chain of their own?
前面,我们定义了区块链就是一个具有共享状态的交易单机。使用这个定义,我们可以知道正确的当前状态是一个全球真相,所有人都必须要接受它。拥有多个状态(或多个链)会摧毁这个系统,因为它在哪个是正确状态的问题上不可能得到统一结果。如果链分叉了,你有可能在一条链上拥有10个币,一条链上拥有20个币,另一条链上拥有40个币。在这种场景下,是没有办法确定哪个链才是最”有效的“。
Before, we defined the block chain as a single machine with a shared status. With this definition, we can know that the correct current state is a global truth, and that everyone has to accept it. Having multiple states (or chains) destroys the system because it is impossible to achieve a uniform result on what is the correct state. If the chain splits, you may have 10 coins in a chain, 20 coins in a chain and 40 coins in another. In this scenario, there is no way to determine which chain is the most effective.
不论什么时候只要多个路径产生了,一个”分叉“就会出现。我们通常都想避免分叉,因为它们会破坏系统,强制人们去选择哪条链是他们相信的链。
Whenever multiple paths are created, one fork appears. We usually try to avoid a fork, because they destroy the system and force people to choose which chain they believe.
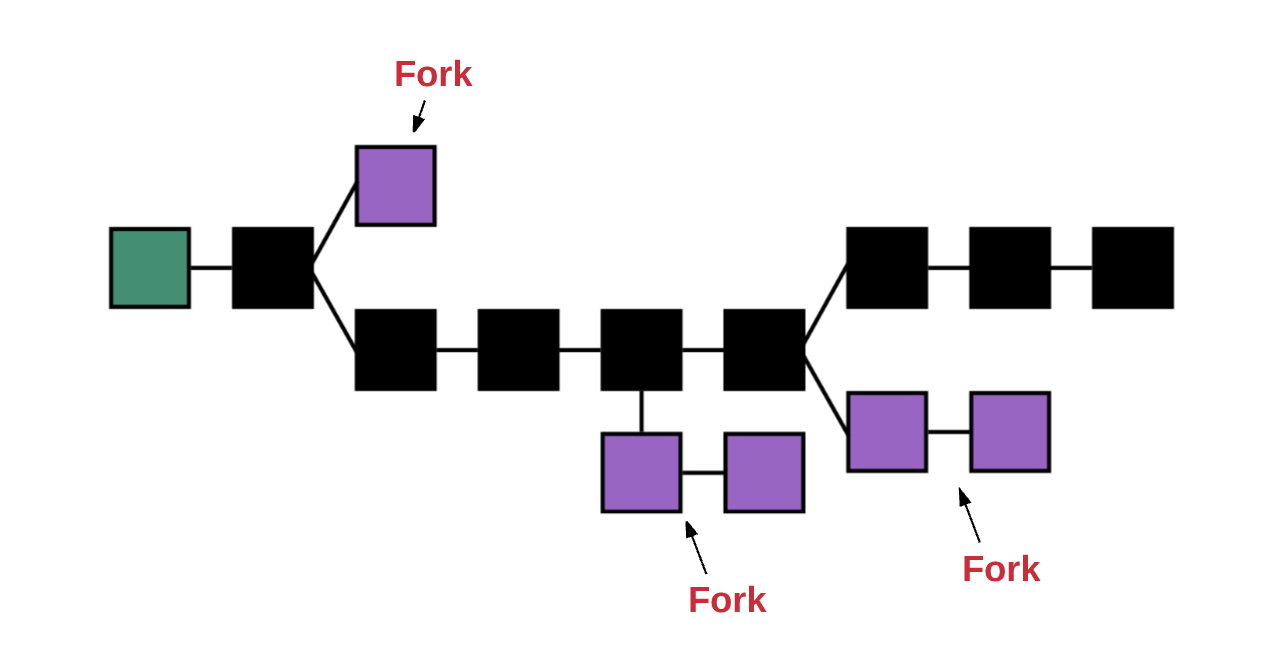
为了确定哪个路径才是最有效的以及防止多条链的产生,以太坊使用了一个叫做“GHOST协议(GHOST protocol.)”的数学机制。
In order to determine which path is the most effective and to prevent the creation of multiple chains, Etheria uses a mathematical mechanism called “GHOST protocol.”.
GHOST=Greedy Heaviest Observed Subtree
简单来说,GHOST协议就是让我们必须选择一个在其上完成计算最多的路径。一个方法确定路径就是使用最近一个区块(叶子区块)的区块号,区块号代表着当前路径上总的区块数(不包含创世纪区块)。区块号越大,路径就会越长,就说明越多的挖矿算力被消耗在此路径上以达到叶子区块。使用这种推理就可以允许我们赞同当前状态的权威版本。
Simply put, the GHOST agreement makes us have to choose a path on which most calculations are made. One way to determine the path is to use the number of blocks of the last block (leaf blocks), which represents the total number of blocks on the current path (not containing the original blocks). The larger the block number, the longer the path, the more the value of the dig is consumed in this path to reach the leaf blocks. Using this reasoning would allow us to endorse the authoritative version of the current state.
现在你大概对区块链是什么有个理性的认识,让我们在再深入了地解一下以太坊系统主要组成部分:
Now you probably have a rational understanding of what the chain of blocks is, so let's go further and explain the main components of the Etheraya system:
账户(accounts)
Accounts (accounts)
状态(state)
Status
损耗和费用(gas and fees)
Losses and costs (gas and Fees)
交易(transactions)
Transactions
区块(blocks)
Blocks (blocks)
交易执行(transaction execution)
Transactions execution
挖矿(mining)
Mining (mining)
工作量证明(proof of work)
Workload certification (proof of work)
在开始之前需要注意的是:每当我说某某的hash, 我指的都是KECCAK-256 hash, 以太坊就是使用这个hash算法。
What needs to be noted before we start is that every time I say "hash," I'm talking about KECAK-256 hash, which is what Etherwood uses.
账户
Account
以太坊的全局“共享状态”是有很多小对象(账户)来组成的,这些账户可以通过消息传递架构来与对方进行交互。每个账户都有一个与之关联的状态(state)和一个20字节的地址(address)。在以太坊中一个地址是160位的标识符,用来识别账户的。
Each account has a state associated with it and a 20 byte address (address). One address in the district is a 160-bit identifier to identify the account.
这是两种类型的账户:
These are two types of accounts:
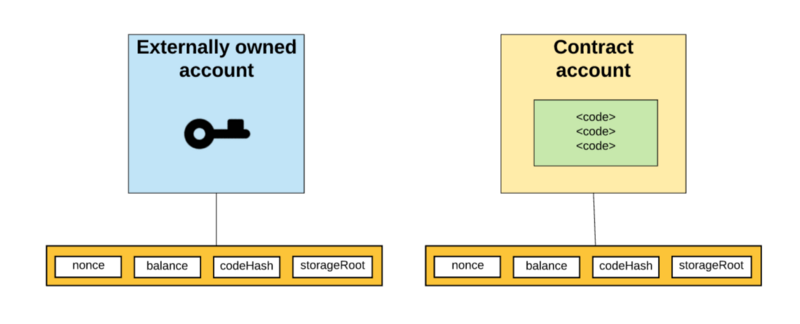
外部拥有的账户,被私钥控制且没有任何代码与之关联
Externally owned accounts that are controlled by private keys without any code associated with them
合约账户,被它们的合约代码控制且有代码与之关联
Contract accounts, controlled by and linked to their contract code.
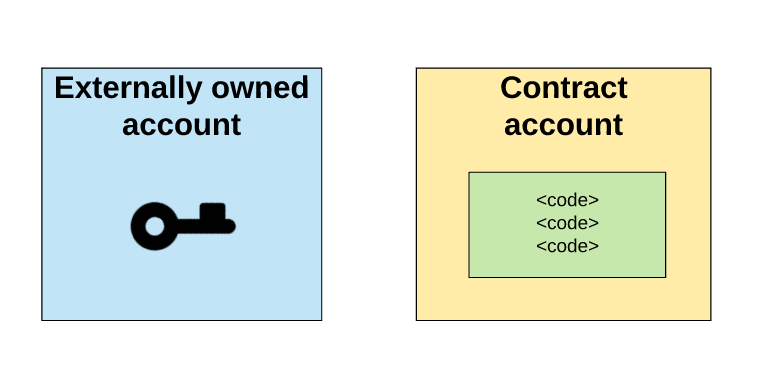
外部拥有账户与合约账户的比较
Comparison of externally owned and contracted accounts
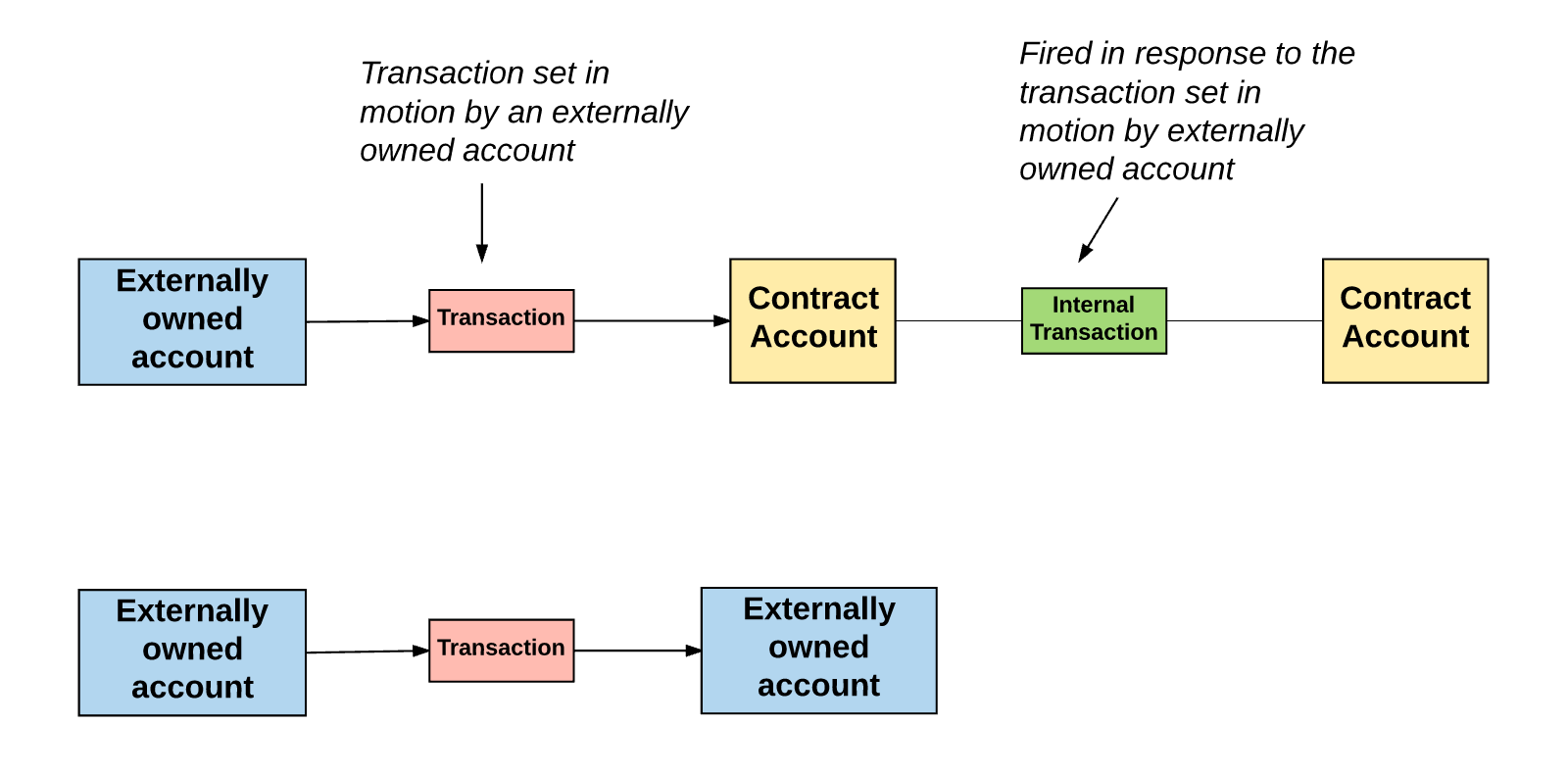
理解外部拥有账户和合约账户的基本区别是很重要的。一个外部拥有账户可以通过创建和用自己的私钥来对交易进行签名,来发送消息给另一个外部拥有账户或合约账户。在两个外部拥有账户之间传送的消息只是一个简单的价值转移。但是从外部拥有账户到合约账户的消息会激活合约账户的代码,允许它执行各种动作。(比如转移代币,写入内部存储,挖出一个新代币,执行一些运算,创建一个新的合约等等)。
It is important to understand the basic difference between external ownership and contractual accounts. An externally owned account can send a message to another externally owned account or contractual account by creating and signing a transaction with its own private key. A message transmitted between two externally owned accounts is a simple transfer of value. But a message from external ownership to a contractual account activates the code of the contractual account and allows it to perform various actions (e.g. transfer money, internal storage, digging out a new currency, performing some calculations, creating a new contract, etc.).
不像外部拥有账户,合约账户不可以自己发起一个交易。相反,合约账户只有在接收到一个交易之后(从一个外部拥有账户或另一个合约账户接),为了响应此交易而触发一个交易。我们将会在“交易和消息”部分来了解关于合约与合约之间的通信。
Unlike externally owned accounts, a contractual account cannot initiate a transaction itself. Instead, a contractual account triggers a transaction in response to a transaction only after it has been received (from an externally owned account or from another contractual account). We will learn about the communication between the contract and the contract in the “transactions and messages” section.
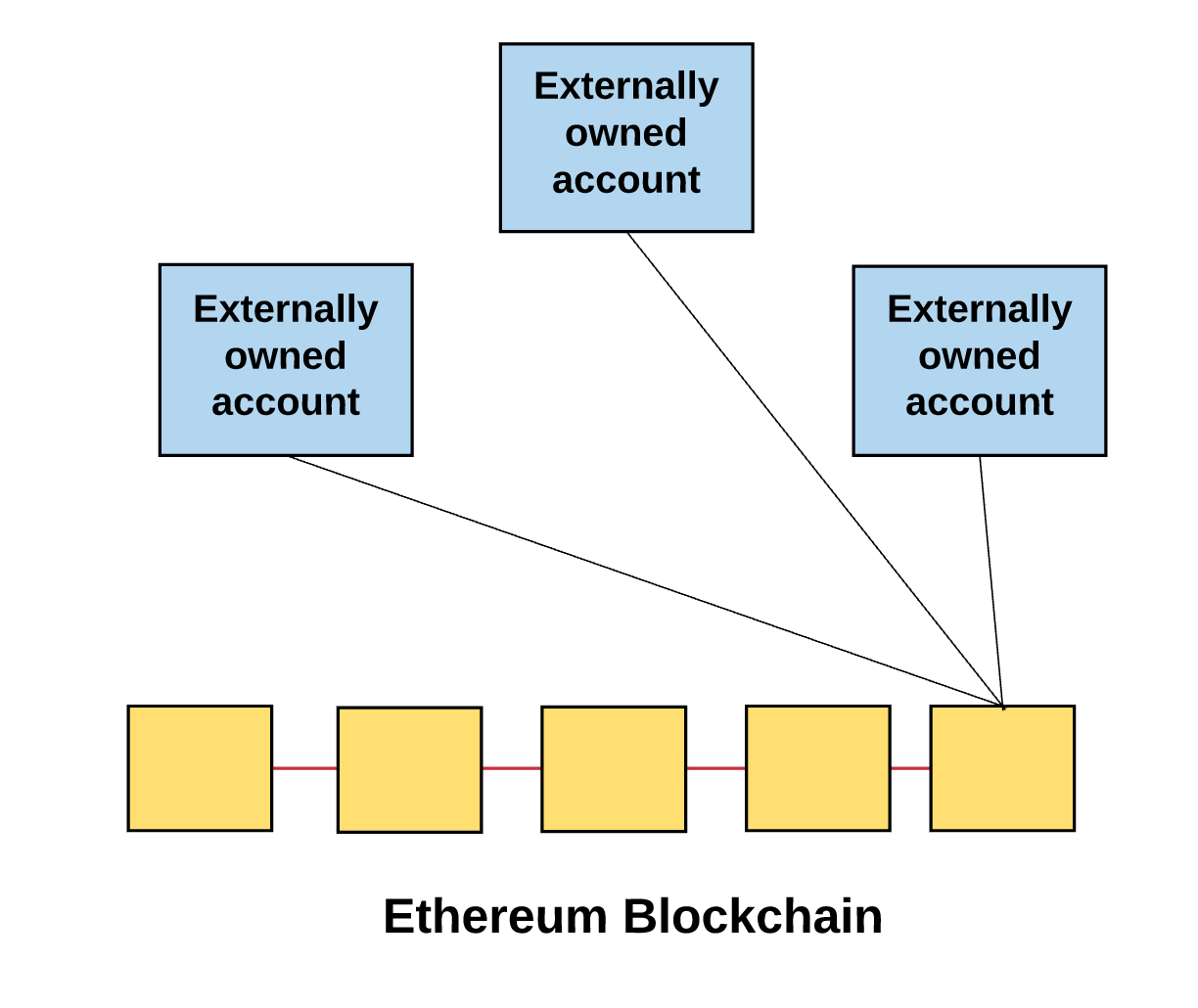
因此,在以太坊上任何的动作,总是被外部控制账户触发的交易所发动的。
Therefore, any movement in the Etherm is always triggered by an exchange triggered by an externally controlled account.
账户状态
Account Status
账户状态有四个组成部分,不论账户类型是什么,都存在这四个组成部分:
There are four components in the account status, regardless of the account type:
nonce:如果账户是一个外部拥有账户,nonce代表从此账户地址发送的交易序号。如果账户是一个合约账户,nonce代表此账户创建的合约序号
If the account is an externally owned account, nonce represents the transaction number from the account address. If the account is a contractual account, nonce represents the contract number created by the account
balance: 此地址拥有Wei的数量。1Ether=10^18Wei
Balance: This address has the number of Wei.
storageRoot: Merkle Patricia树的根节点Hash值(我们后面在解释Merkle树)。Merkle树会将此账户存储内容的Hash值进行编码,默认是空值
The Merkle tree encodes the Hash value of the contents of this account, defaulting on empty values.
codeHash:此账户EVM(以太坊虚拟机,后面细说)代码的hash值。对于合约账户,就是被Hash的代码并作为codeHash保存。对于外部拥有账户,codeHash域是一个空字符串的Hash值
code hash. For contractual accounts, the code is saved as code Hash. For externally owned accounts, the codeHash field is an empty Hash value of a string.
世界状态
State of the world
好了,我们知道了以太坊的全局状态就是由账户地址和账户状态的一个映射组成。这个映射被保存在一个叫做Merkle Patricia树的数据结构中
Well, we know that Ether's global state is a map of the account address and account status. This map is stored in a data structure called Merkle Patricia's tree.
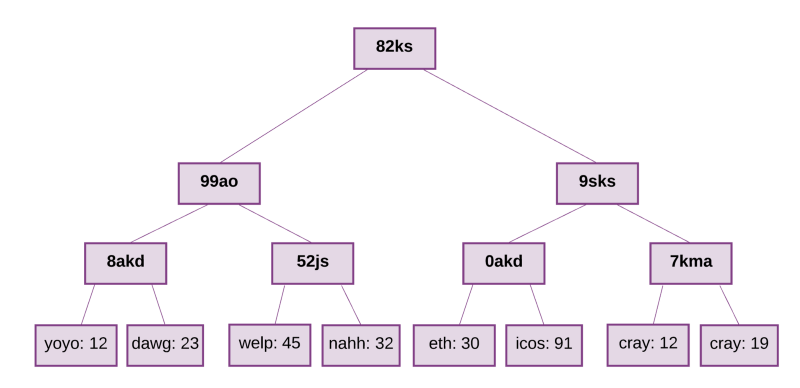
Merkle Tree(也被叫做Merkle trie)是一种由一系列节点组成的二叉树,这些节点包括:
Merkle Tree (also known as Merkle Trie) is a two-fork tree made up of a series of nodes, which include:
在树底的包含了源数据的大量叶子节点
There's a lot of leaves at the bottom of the tree that contain source data.
一系列的中间的节点,这些节点是两个子节点的Hash值
A series of mid-point nodes, these nodes are the two sub-nodes' Hash values.
一个根节点,同样是两个子节点的Hash值,代表着整棵树
One root node, the same two subnominal Hash value, represents the whole tree.
树底的数据是通过分开我们想要保存到chunks的数据产生的,然后将chunks分成buckets,再然后再获取每个bucket的hash值并一直重复直到最后只剩下一个Hash:根Hash。
The data at the bottom of the tree is generated by separating the data that we want to save to chunks, and then dividing the chunks into buckets, and then recapitulating the hash values of each bucket and repeating them until there is only one Hash: root Hash.
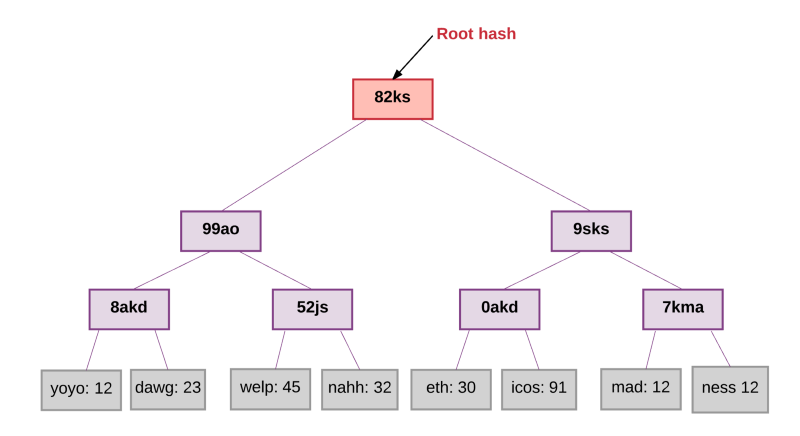
这棵树要求存在里面的值(value)都有一个对应的key。从树的根节点开始,key会告诉你顺着哪个子节点可以获得对应的值,这个值存在叶子节点。在以太坊中,key/value是地址和与地址相关联的账户之间状态的映射,包括每个账户的balance, nonce, codeHash和storageRoot(storageRoot自己就是一颗树)。
This tree requires that there be a corresponding key value. Starting with the root node of the tree, Key will tell you which sub-node is followed by the corresponding value, which has a leaf node. In Ether, Key/value is a map of the state between the address and the account associated with the address, including the ballance, nonece, codeHash and the treeRoot (the tree itself).
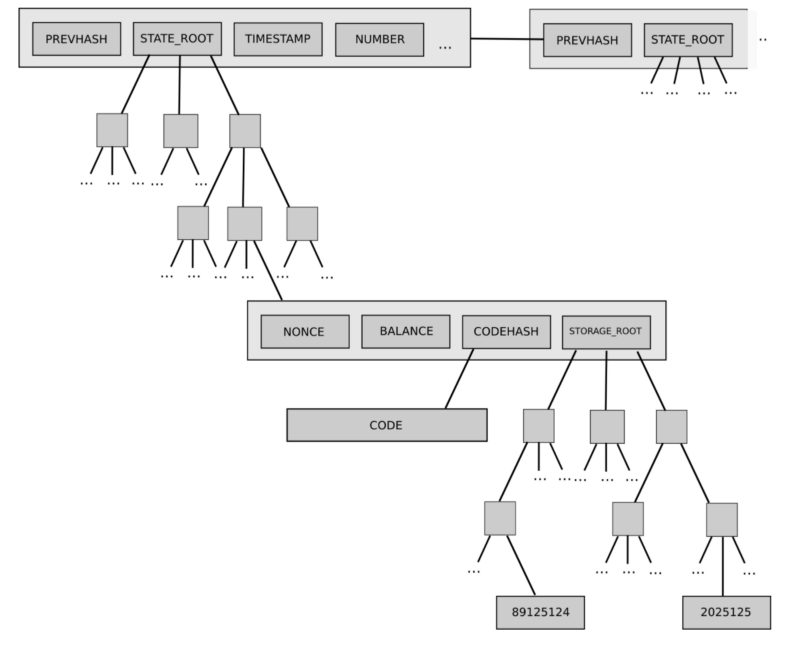
同样的树结构也用来存储交易和收据。更具体的说,每个块都有一个头(header),保存了三个不同Merkle trie结构的根节点的Hash,包括:
The same tree structure is also used to store transactions and receipts. More specifically, each block has a head (header) and saves the Hash, which is the root of three different Merkle Trie structures, including:
状态树
Status Tree
交易树
Trade Tree
收据树
The receipts tree.
在Merkle tries中存储所有信息的高效性在以太坊中的“轻客户端”和“轻节点”相当的有用。记住区块链就是一群节点来维持的。广泛的说,有两种节点类型:全节点和轻节点。
The efficiency of storing all information in Merkle Tries is quite useful in the “light client” and “light node” in the ether chamber. Remember that block chains are maintained by a group of nodes. Broadly speaking, there are two types of nodes: full nodes and light nodes.
全节点通过下载整条链来进行同步,从创世纪块到当前块,执行其中包含的所有交易。通常,矿工会存储全节点,因为他们在挖矿过程中需要全节点。也有可能下载一个全节点而不用执行所有的交易。无论如何,一个全节点包含了整个链。
The whole node is synchronized by downloading the whole chain, from Genesis block to the present block, executing all the transactions contained in it. Usually, the unions store the whole node because they need the whole node during the mining process. It is also possible to download a whole node instead of executing all the transactions. In any case, a whole node contains the whole chain.
不过除非一个节点需要执行所有的交易或轻松访问历史数据,不然没必要保存整条链。这就是轻节点概念的来源。比起下载和存储整个链以及执行其中所有的交易,轻节点仅仅下载链的头,从创世纪块到当前块的头,不执行任何的交易或检索任何相关联的状态。由于轻节点可以访问块的头,而头中包含了3个tries的Hash,所有轻节点依然可以很容易生成和接收关于交易、事件、余额等可验证的答案。
However, there is no need to preserve the entire chain unless a node needs to execute all transactions or easy access to historical data. That is the source of the light node concept. Compared to downloading and storing the entire chain and executing all transactions therein, the light node simply downloads the head of the chain, from the beginning of the century to the head of the current block, does not execute any transaction or retrieve any associated state. Since the light node can access the head of the block, the head contains the Hash of three tries, all light nodes can still easily generate and receive verifiable answers on transactions, events, balances, etc.
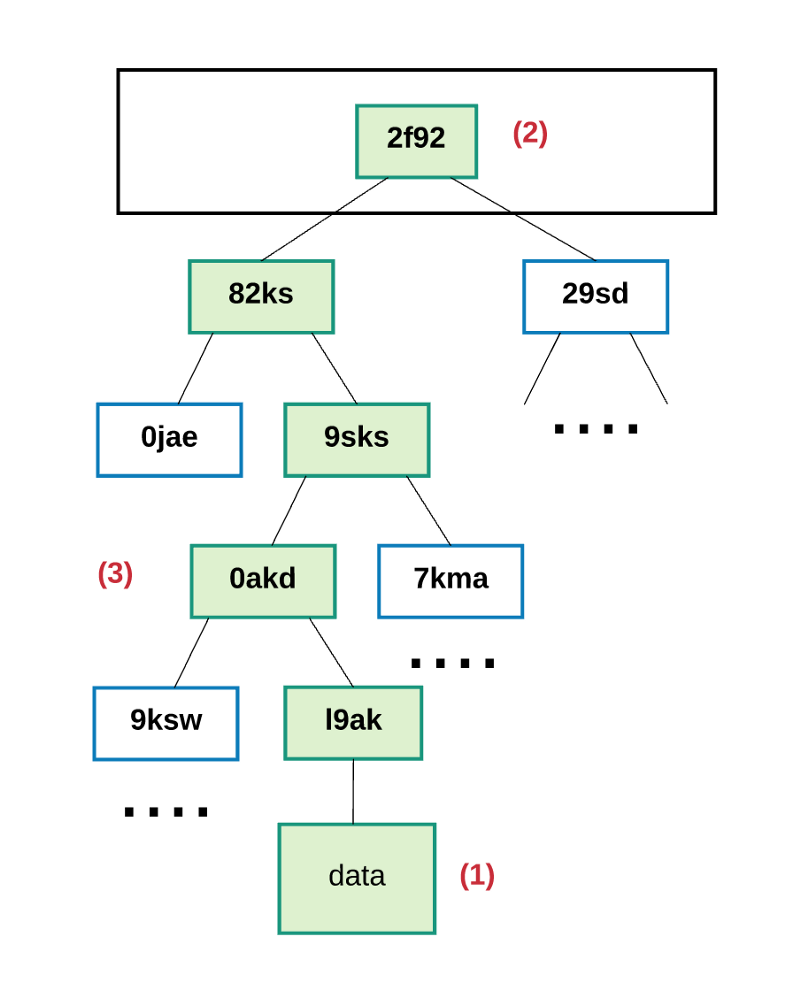
这个可以行的通是因为在Merkle树中hash值是向上传播的-如果一个恶意用户试图用一个假交易来交换Merkle树底的交易,这个会改变它上面节点的hash值,而它上面节点的值的改变也会导致上上一个节点Hash值的改变,以此类推,一直到树的根节点。
This can be achieved because the hash value in the Merkle tree is transmitted upwards - if a malicious user tries to exchange a fake transaction for a transaction at the bottom of the Merkle tree, this will change the hash value at the top of the node, and the change in the value at the top of the node will also result in a change in the last node Hash value, and so on until the root node of the tree.
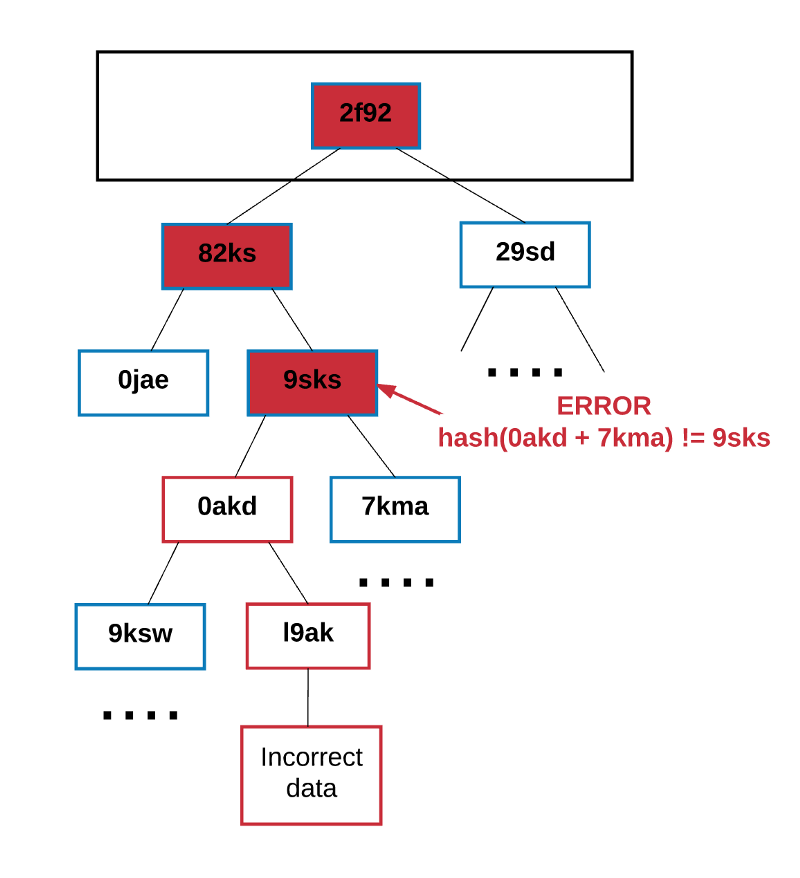
任何节点想要验证一些数据都可以通过Merkle证明来进行验证,Merkle 证明的组成:
Any node that wants to verify some data can be validated by Merkle certification, which consists of:
一块需要验证的数据
A piece of data to verify
树的根节点Hash
The root of the tree, Hash.
一个“分支”(从 chunk到根这个路径上所有的hash值)
A branch (all hash values from chunk to root)
任何可以读取证明的人都可以验证分支的hash是连贯的,因此给出的块在树中实际的位置就是在此处。
Anyone who can read the certificate can verify that the branch hash is coherent, so the given block is actually located in the tree here.
总之,使用Merkle Patricia树的好处就是该结构的根节点加密取决于存储在树中的数据,而且根据点的hash还可以作为该数据的安全标识。由于块的头包含了状态、交易、收据树的根hash,所有任何节点都可以验证以太坊的一小部分状态而不用保存整个状态,这整个状态的的大小可能是非常大的。
In short, the advantage of using the Merkle Patricia tree is that the root node encryption of the structure depends on the data stored in the tree and can also be used as a security mark for the data according to the hash of the point. Since the head of the block contains the roots of the status, transaction, receipt tree shash, all nodes can verify a small part of the position in the Taiku instead of preserving the whole state, which may be very large.
Gas和费用
Gas and costs
在以太坊中一个比较重要的概念就是费用(fees),由以太坊网络上的交易而产生的每一次计算,都会产生费用-没有免费的午餐。这个费用是以称之为”gas”的来支付。
One of the more important concepts in Etheria is the cost (fees), which is paid for by what is known as the "gas" for every transaction on the Ethionet.
gas就是用来衡量在一个具体计算中要求的费用单位。gas price就是你愿意在每个gas上花费Ether的数量,以“gwei”进行衡量。“Wei”是Ether的最小单位,1Ether表示10^18Wei. 1gwei是1.000.000.000 Wei。
Gas is the unit of cost that is required in a specific calculation. Gas price is your willingness to spend the amount of Ether on each gas, as measured by “gwei”. “Wei” is the smallest unit of Ether, and 1Ether is the 10⁄18wei. 1gwei is 1.00.00.00.000 Wei.
对每个交易,发送者设置gas limit和gas price。gas limit和gas price就代表着发送者愿意为执行交易支付的Wei的最大值。
For each transaction, the sender sets the maximum value of Gas limit and gas price. Gas limit and gas price represent the maximum value of Wei that the sender is willing to pay to execute the transaction.
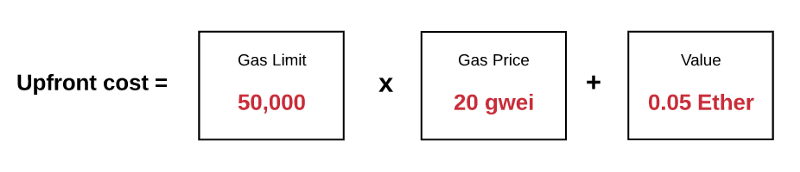
例如,假设发送者设置gas limit为50.000.gas price为20gwei。这就表示发送者愿意最多支付50.000*20gwei=1.000.000.000.000.000 Wei=0.001 Ether来执行此交易。
For example, it is assumed that the sender will set gas limit at 50.00.gas price at 20 gwei. This means that the sender is willing to pay up to 50,000*20gwei = 1.000.000.00.00.000 Wei = 0.001 Ether to carry out the transaction.
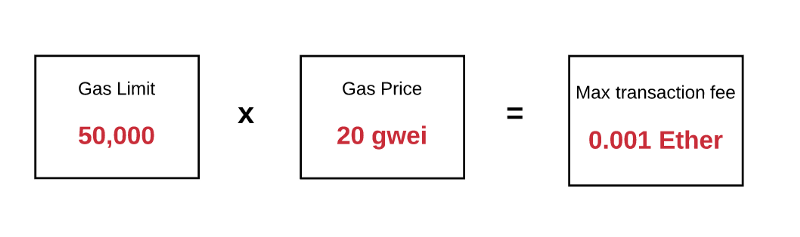
记住gas limit代表用户愿意花费在gas上的钱的最大值。如果在他们的账户余额中有足够的Ether来支付这个最大值费用,那么就没问题。在交易结束时任何未使用的gas都会被返回给发送者,以原始费率兑换。
Remember that gas limit represents the maximum value of money that users would like to spend on gas. If there is enough rest in their account balance to cover this maximum cost, then it will be fine. Any unused gass will be returned to the sender at the end of the transaction for exchange at the original rate.
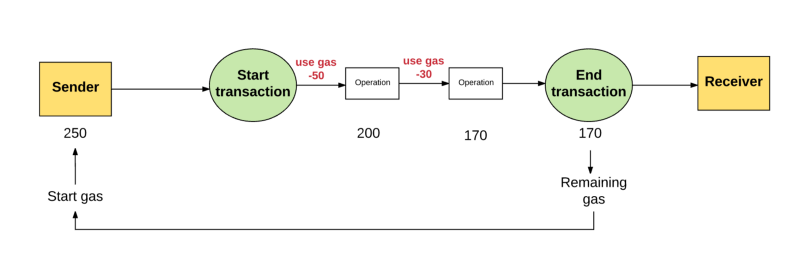
在发送者没有提供足够的gas来执行交易,那么交易执行就会出现“gas不足”然后被认为是无效的。在这种情况下,交易处理就会被终止以及所有已改变的状态将会被恢复,最后我们就又回到了交易之前的状态-完完全全的之前状态就像这笔交易从来没有发生。因为机器在耗尽gas之前还是为计算做出了努力,
When the sender fails to provide enough gas to execute the transaction, the transaction is “gas deficient” and then considered invalid. In this case, the transaction is terminated and all changed status will be restored, and in the end we return to the pre-trading state -- the pre-complete state is as if the transaction had never occurred.
所以理论上,将不会有任何的gas被返回给发送者。
In theory, therefore, there will not be any gas to be returned to the sender.
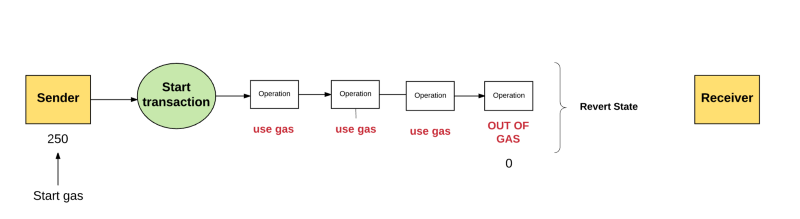
这些gas的钱到底去了哪里?发送者在gas上花费的所有钱都发送给了“受益人”地址,通常情况下就是矿工的地址。因为矿工为了计算和验证交易做出了努力,所以矿工接收gas的费用作为奖励。
Where's the gas money? All the money that the sender spends on the gas was sent to the “beneficiary” address, usually the miner's address.
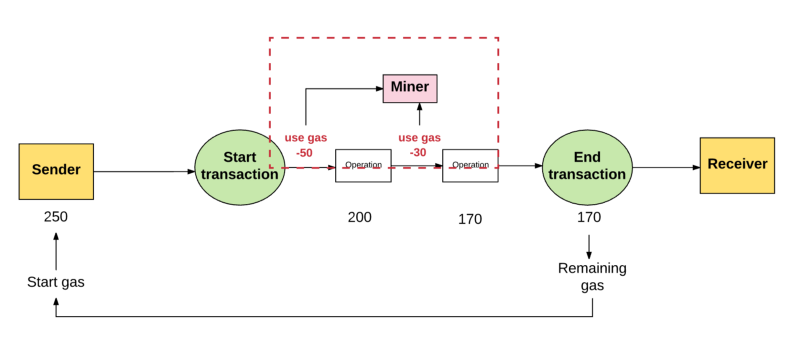
通常,发送者愿意支付更高的gas price,矿工从这笔交易总就能获得更多的价值。因此,矿工也就更加愿意选择这笔交易。这样的话,矿工可以自由的选择一笔交易自己愿意验证或忽略。为了引导发送者应该设置gas price为多少,矿工可以选择建议一个最小的gas值他们愿意执行一个交易。
Usually, the sender is willing to pay a higher gas price, and the miners always get more value from the deal. So the miners are more willing to choose the deal. In that case, the miners are free to choose a deal that they want to verify or ignore. To guide the sender to what it should be, the miners can choose to recommend a minimum gas value for a transaction.
存储也有费用
There's a cost to storage.
gas不仅仅是用来支付计算这一步的费用,而且也用来支付存储的费用。存储的总费用与所使用的32位字节的最小倍数成比例。
Gas is used not only to cover the cost of calculating this step, but also to cover the cost of storage. The total cost of storage is proportional to the minimum multiplier of the 32-bit bytes used.
存储费用有一些比较细微的方面。比如,由于增加了的存储增加了所有节点上的以太坊状态数据库的大小,所以激励保持数据存储量小。为了这个原因,如果一个交易的执行有一步是清除一个存储实体,那么为执行这个操作的费用就会被放弃,并且由于释放存储空间的退款就会被返回给发送者。
For example, because increased storage increases the size of an Ether-state database at all nodes, incentives are given to keep data stored in small quantities. For this reason, if a transaction is executed one step away from a storage entity, the cost of doing so will be abandoned, and refunds of the storage space will be returned to the sender as they are released.
费用的作用是什么?
What does the cost do?
以太坊可以运作的一个重要方面就是每个网络执行的操作同时也被全节点所影响。然而,计算的操作在以太坊虚拟机上是非常昂贵的。因此,以太坊智能合约最好是用来执行最简单的任务,比如运行一个简单的业务逻辑或者验证签名和其他密码对象,而不是用于复杂的操作,比如文件存储,电子邮件,或机器学习,这些会给网络造成压力。施加费用防止用户使网络超负荷。
An important aspect of Ether's functioning is that the operations performed by each network are also influenced by the full node. However, computing operations are very expensive on Ether's virtual machine. Therefore, Ether's smart contracts are best used to carry out the simplest tasks, such as running a simple business logic or validating signatures and other password objects, rather than complex operations, such as document storage, e-mail, or machine learning, which put pressure on the network.
以太坊是一个图灵完备语言(短而言之,图灵机器就是一个可以模拟任何电脑算法的机器。对于图灵机器不太熟悉的人可以看看这个 和这个 )。这就允许有循环,并使以太坊受到停机问题 的影响,这个问题让你无法确定程序是否无限制的运行。如果没有费用的话,恶意的执行者通过执行一个包含无限循环的交易就可以很容易的让网络瘫痪而不会产生任何反响。因此,费用保护网络不受蓄意攻击。
Ether is a perfect language for Turing (in short, the Turing machine is a machine that can simulate any computer algorithm. A person who is not familiar with the Turing machine can look at this and this). This allows circulation and exposes Ether to a shutdown problem, which makes it impossible for you to determine whether the program works indefinitely.
你也许会想,“为什么我们还需要为存储付费?”其实就像计算一样,以太坊网络上的存储是整个网络都必须要负担的成本。
You might think, "Why do we still have to pay for storage?" It's actually, like a calculation, that storage on the web is a cost that the entire network has to pay.
交易和消息
Transactions and messages
之前说过以太坊是一个基于交易的状态机。换句话说,在两个不同账户之间发生的交易才让以太坊全球状态从一个状态转换成另一个状态。
It was said earlier that Ether was a trading-based state machine. In other words, transactions between two different accounts allowed Etherworld to change from one state to another.
最基本的概念,一个交易就是被外部拥有账户生成的加密签名的一段指令,序列化,然后提交给区块链。
The most basic concept is that a transaction is a command, sequenced and then presented to the block chain by an encrypted signature generated by an externally owned account.
有两种类型的交易:消息通信和合约创建(也就是交易产生一个新的以太坊合约)。
There are two types of transactions: message communication and contract creation (i.e. the transaction creates a new Etheria contract).
不管什么类型的交易,都包含:
All types of transactions include:
nonce:发送者发送交易数的计数
Number of transactions sent by sender
gasPrice:发送者愿意支付执行交易所需的每个gas的Wei数量
GasPrice: The sender is willing to pay the amount of Wei per gas required to execute the transaction
gasLimit:发送者愿意为执行交易支付gas数量的最大值。这个数量被设置之后在任何计算完成之前就会被提前扣掉
GasLimit: The sender is willing to pay the maximum amount of gas to execute the transaction.
to:接收者的地址。在合约创建交易中,合约账户的地址还没有存在,所以值先空着
To: The address of the recipient. The address of the contract account does not exist in the contract creation transaction, so the value is empty.
value:从发送者转移到接收者的Wei数量。在合约创建交易中,value作为新建合约账户的开始余额
value: the number of Wei transfers from the sender to the recipient. In the contract creation transaction, value represents the start-up balance of the new contract account
v,r,s:用于产生标识交易发生着的签名
v, r, s: used to generate signatures where the marking transaction is taking place
init(只有在合约创建交易中存在):用来初始化新合约账户的EVM代码片段。init值会执行一次,然后就会被丢弃。当init第一次执行的时候,它返回一个账户代码体,也就是永久与合约账户关联的一段代码。
Init (only exists in the contract creation transaction): the EVM snippet used to initialize the new contract account. The init value is executed once and then discarded. When the init is first executed, it returns an account code body, a code permanently associated with the contract account.
data(可选域,只有在消息通信中存在):消息通话中的输入数据(也就是参数)。例如,如果智能合约就是一个域名注册服务,那么调用合约可能就会期待输入域例如域名和IP地址
Data (optional, only exists in message): input data (i.e. parameters) in message calls. For example, if an intelligent contract is a domain name registration service, the call contract may expect to enter fields such as domain names and IP addresses
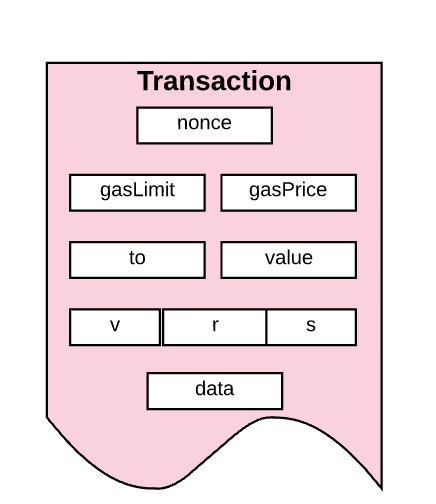
在“账户”这个章节中我们学到交易-消息通信和合约创建交易两者都总是被外部拥有账户触发并提交到区块链的。换种思维思考就是,交易是外部世界和以太坊内部状态的桥梁。
In the "Accounts" chapter, we learn that trade-message communications and contract creation transactions are always triggered by externally owned accounts and submitted to block chains. In other words, trade is a bridge between the outside world and the state within Etheria.
但是这也并不代表一个合约与另一个合约无法通信。在以太坊状态全局范围内的合约可以与在相同范围内的合约进行通信。他们是通过“消息”或者“内部交易”进行通信的。我们可以认为消息或内部交易类似于交易,不过与交易有着最大的不同点-它们不是由外部拥有账户产生的。相反,他们是被合约产生的。它们是虚拟对象,与交易不同,没有被序列化而且只存在与以太坊执行环境。
But this does not mean that one contract cannot communicate with another. Contracts within the context of the Ether chamber can communicate with contracts within the same range. They communicate through “message” or “internal transactions.” We can assume that information or internal transactions are similar to transactions, but the greatest difference with transactions – they are not generated by external ownership accounts. On the contrary, they are created by contracts. They are virtual objects, unlike transactions, are not sequenced and have only an implementation environment with Etheria.
当一个合约发送一个内部交易给另一个合约,存在于接收者合约账户相关联的代码就会被执行。
When one contract sends one internal transaction to another, the code attached to the recipient's contractual account is enforced.
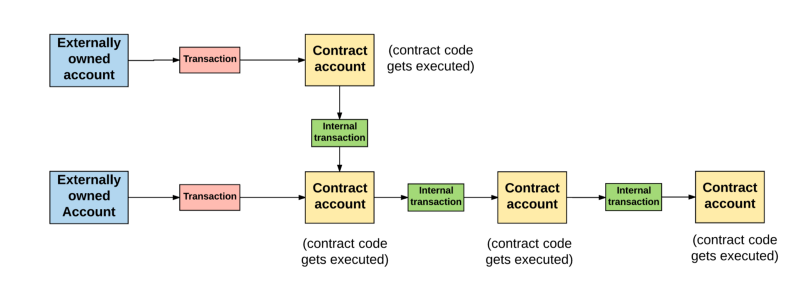
一个重要需要注意的事情是内部交易或者消息不包含gasLimit。因为gas limit是由原始交易的外部创建者决定的(也就是外部拥有账户)。外部拥有账户设置的gas limit必须要高到足够将交易完成,包括由于此交易而长生的任何”子执行”,例如合约到合约的消息。如果,在一个交易或者信息链中,其中一个消息执行使gas已不足,那么这个消息的执行会被还原,包括任何被此执行触发的子消息。不过,父执行没必要被还原。
One important thing to note is that internal transactions or messages do not include gasLimit. Because gas limit is determined by the external creator of the original transaction (i.e., by external ownership of the account). Gas limits with external ownership of the account set must be high enough to complete the transaction, including any "sub-execution" that is a permanent consequence of the transaction, such as the contract-to-contract message. If, in a transaction or information chain, the implementation of one of the messages is inadequate, the message will be returned, including any sub-information triggered by the execution.
区块
Blocks
所有的交易都被组成一个”块”。一个区块链包含了一系列这样的链在一起区块。
All transactions are made into a block. A block chain contains a series of such chains of blocks together.
在以太坊中,一个区块包含:
In Etheria, one block contains:
区块头
Blockhead
关于包含在此区块中交易集的信息
Information about the transaction set contained in this block
与当前块的ommers相关的一系列其他区块头
A range of other blocks associated with the current block's ommer's
Ommers解释
Ommers explains.
“ommer”到底是什么? ommer就是一个区块的父区块与当前区块父区块的父区块是相同的。让我们快速了解一下ommers是用来干嘛的,并且为什么一个区块需要为ommers包含区块头。
Ommer is the parent block of a block that is the same as the parent block of the current block. Let us quickly see what the ommeres are for, and why a block needs to contain the head of the block for the ommers.
由于以太坊的构造,它的区块生产时间(大概15秒左右)比其他的区块链例如Bitcoin(大概10分钟左右)要快很多。这使得交易的处理更快。但是,更短的区块生产时间的一个缺点就是:更多的竞争区块会被矿工发现。这些竞争区块同样也被称为“孤区块”(也就是被挖出来但是不会被添加到主链上的区块)。
Because of its construction, the block production time (about 15 seconds) is much faster than the other block chains, such as Bitcoin (about 10 minutes). This makes the deal quicker. But one of the disadvantages of the shorter block production time is that more competing blocks will be discovered by miners.
Ommers的目的就是为了帮助奖励矿工纳入这些孤区块。矿工包含的ommers必须是有效的,也就是ommers必须在父区块的第6个子区块之内或更小范围内。在第6个子区块之后,陈旧的孤区块将不会再被引用(因为包含老旧的交易会使事情变得复杂一点)。
Ommers is designed to help reward miners for including these blocks. The miners must contain ommers, that is, ommers must be within or within the sixth sub-block of the parent block. After the sixth sub-block, the old ones will not be cited again (because the inclusion of older transactions makes matters a little more complicated).
Ommer区块会收到比全区块少一点的奖励。不管怎样,依然存在激励来让矿工们纳入孤区块并能从中获得一些报酬。
Ommer blocks receive less rewards than the whole block. In any case, incentives exist for miners to be integrated into the block and receive some compensation from it.
区块头
Blockhead
让我们再回到区块的问题上。我们前面提到每个区块都有一个“区块头”,但这究竟是什么?
Let's go back to the block. We mentioned that each block has a block, but what is it?
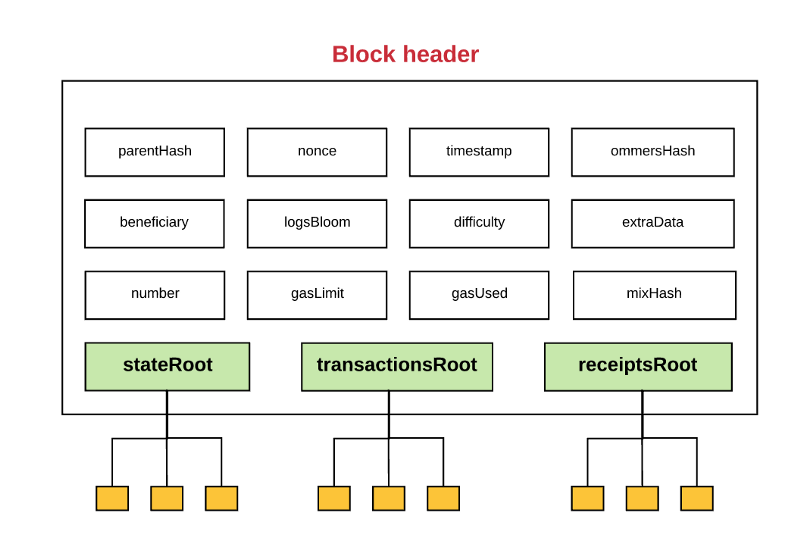
区块头是一个区块的一部分,包含了:
The block head is part of a block consisting of:
parentHash:父区块头的Hash值(这也是使得区块变成区块链的原因)
ParentHash: The Hash value of the head of the parent block (which is also the reason why the block becomes a chain of blocks)
ommerHash:当前区块ommers列表的Hash值
ommerHash: Hash values from the current block ommers list
beneficiary:接收挖此区块费用的账户地址
Beneficiary: account address to receive the cost of digging this block
stateRoot:状态树根节点的Hash值(回忆一下我们之前所说的保存在头中的状态树以及它使得轻客户端认证任何关于状态的事情都变得非常简单)
QueRoot: The Hash value of the state root node (remember what we said about the state tree in the head and it makes it very simple for the light client to authenticate anything about the state)
transactionsRoot:包含此区块所列的所有交易的树的根节点Hash值
TransactionsRoot: Root Hash values of trees containing all transactions listed in this block
receiptsRoot:包含此区块所列的所有交易收据的树的根节点Hash值
ReceiptsRoot: Root Hash value of a tree containing all transaction receipts listed in this block
logsBloom:由日志信息组成的一个Bloom过滤器 (数据结构)
logsBloom: a Bloom filter (data structure) consisting of log information
difficulty: 此区块的难度级别
difficulty: difficulty level of this block
number:当前区块的计数(创世纪块的区块序号为0.对于每个后续区块,区块序号都增加1)
Number: Number of current blocks (the number of blocks in the original block is 0. For each subsequent block, the number of blocks is increased by 1)
gasLimit:每个区块的当前gas limit
GasLimit: Current gas limit for each block
gasUsed: 此区块中交易所用的总gas量
GasUsed: Total number of gass used for transactions in this block
timestamp:此区块成立时的unix的时间戳
Timestamp: Unix stamp when this block was formed
extraData:与此区块相关的附加数据
ExtraData: Additional data relevant to this block
mixHash:一个Hash值,当与nonce组合时,证明此区块已经执行了足够的计算
MixHash: a Hash value which, when combined with nance, proves that the block has performed sufficient calculations
nonce:一个Hash值,当与mixHash组合时,证明此区块已经执行了足够的计算
Nonce: a Hash value which, when combined with MixHash, proves that the block has performed sufficient calculations
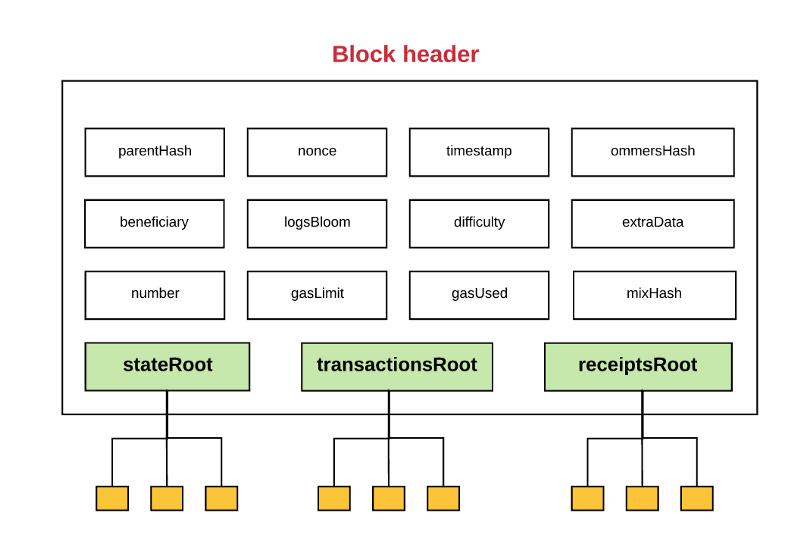
注意每个区块是如何包含三个树结构的,三个树结构分别对应:
Note how each block contains three tree structures, each corresponding to:
状态(stateRoot)
StateRoot
交易(transactionsRoot)
Trading (transactionsRoot)
收据(receiptsRoot)
Receipts (receiptsRoot)
这三个树结构就是我们前面讨论的Merkle Patricia树。
These three tree structures are the Merkle Patricia trees that we discussed earlier.
另外,上面描述的有几个术语值得说明一下,下面来看一下。
In addition, several of the terms described above are worthy of clarification, as will be seen below.
日志
Log
以太坊允许日志可以跟踪各种交易和信息。一个合约可以通过定义“事件”来显示的生成日志。
Ether allows logs to track transactions and information.
一个日志的实体包含:
An entity for a log consists of:
记录器的账户地址
Account address of the recorder
代表本次交易执行的各种事件的一系列主题以及与这些事件相关的任何数据
A series of themes representing events carried out in the context of the transaction and any data related to those events
日志被保存在bloom过滤器 中,过滤器高效的保存了无尽的日志数据。
Logs are stored in the Bloom filter, which efficiently saves endless log data.
交易收据
Transaction receipts
自于被包含在交易收据中的日志信息存储在头中。就像你在商店买东西时收到的收据一样,以太坊为每笔交易都产生一个收据。像你期望的那样,每个收据包含关于交易的特定信息。这些收据包含着:
Since the log information contained in the transaction receipt is stored in the head. Just like the receipt you received at the store when you bought it, the takatoas produce a receipt for every transaction. As you expect, each receipt contains specific information about the transaction. These receipts contain:
区块序号
Block number
区块Hash
Block Hash
交易Hash
The deal's Hash.
当前交易使用了的gas
Gas used in the current transaction
在当前交易执行完之后当前块使用的累计gas
Cumulative use of the current block after the current transaction is completed
执行当前交易时创建的日志
Log created while executing the current transaction
等等
Wait.
区块难度
Block Difficulty
区块的难度是被用来在验证区块时加强一致性。创世纪区块的难度是131.072.有一个特殊的公式用来计算之后的每个块的难度。如果某个区块比前一个区块验证的更快,以太坊协议就会增加区块的难度。
The difficulty of blocks is that they are used to enhance consistency when they are validated. The difficulty of creating blocks is that there is a special formula for calculating each block after they are. If a block is tested faster than the previous block, a Taiyan agreement increases the difficulty of blocks.
区块的难度影响nonce,它是在挖矿时必须要使用proof-of-work算法来计算的一个hash值。
The difficulty of blocks affects nence, which is a hash value that must be calculated using the proof-of-work algorithm for mining purposes.
区块难度和nonce之间的关系用数学形式表达就是:
The relationship between block difficulty and nance is expressed mathematically:
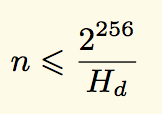
Hd代表的是难度。
Hd represents difficulty.
找到符合难度阈值的nonce唯一方法就是使用proof-of-work算法来列举所有的可能性。找到解决方案预期时间与难度成正比-难度越高,找到nonce就越困难,因此验证一个区块也就越难,这又相应地增加了验证新块所需的时间。所以,通过调整区块难度,协议可以调整验证区块所需的时间。
The only way to find a nonce that meets the difficulty threshold is to use the proof-of-work algorithm to list all possibilities. The more difficult it is to find a solution, the harder it is to find a block, the harder it is to verify a block, which in turn increases the time required to verify a new block. So, by adjusting a block to be difficult, the protocol can adjust the time required to verify a block.
另一方面,如果验证时间变的越来越慢,协议就会降低难度。这样的话,验证时间自我调节以保持恒定的速率-平均每15s一个块。
On the other hand, if the validation time changes more and more slowly, the protocol will be less difficult. In this case, the validation time self-regulates to maintain a constant rate - an average of 15s per block.
交易执行
Transaction execution
我们已经到了以太坊协议最复杂的部分:交易的执行。假设你发送了一笔交易给以太坊网络处理,将以太坊状态转换成包含你的交易这个过程到底发生了什么?
We have reached the most complex part of the Etherton agreement: the execution of the transaction. Assuming that you sent a deal to the Etherton network for processing, what happened to the process of converting the etherpant status into a deal that included you?
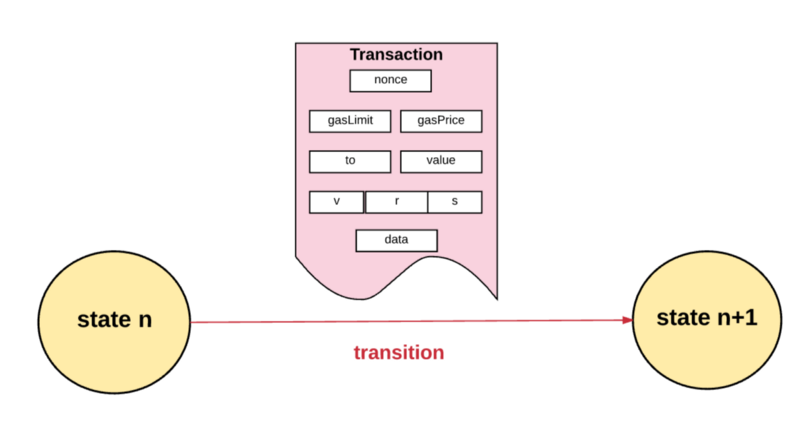
首先,为了可以被执行所有的交易必须都要符合最基础的一系列要求,包括:
First, in order for all transactions to be enforceable, they must meet the most basic set of requirements, including:
交易必须是正确格式化的RLP。”RLP”代表Recursive Length Prefix,它是一种数据格式,用来编码二进制数据嵌套数组。以太坊就是使用RLP格式序列化对象。
The transaction must be a properly formatted RLP. RLP represents Recursive Length Prefix, which is a data format that encodes binary data nesting arrays. Tails are sorted objects using RLP formatting.
有效的交易签名。
Valid transaction signature.
有效的交易序号。回忆一下账户中的nonce就是从此账户发送出去交易的计数。如果有效,那么交易序号一定等于发送账户中的nonce。
A valid transaction number. Remember that nence in the account is the number of transactions sent out from this account. If it is valid, the transaction number must be the same as nence in the send account.
交易的gas limit 一定要等于或者大于交易使用的intrinsic gas,intrinsic gas包括:
Gas limit of the transaction must be equal to or greater than the intrinsic gas, intrinsic gas used in the transaction:
——-1.执行交易预订费用为21.000gas
--1. Implementation of transaction booking costs of 21.000gas
——-2.随交易发送的数据的gas费用(每字节数据或代码为0的费用为4gas,每个非零字节的数据或代码费用为68gas)
—-2. Gas costs for data sent with transactions (4 Gas per byte data or code 0 and 68 Gas per non-zero byte data or code)
——-3.如果交易是合约创建交易,还需要额外的32.000gas
--3. If the transaction is a contract creation transaction, additional 32.000gas will be required
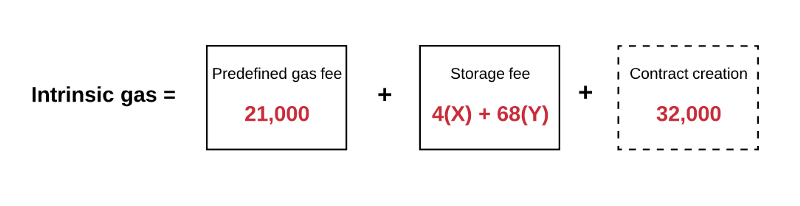
发送账户余额必须有足够的Ether来支付”前期”gas费用。前期gas费用的计算比较简单:首先,交易的gas limit乘以交易的gas价格得到最大的gas费用。然后,这个最大gas费用被加到从发送方传送给接收方的总值。
The balance of the sending account must be sufficient to cover “prior period” gas costs. The calculation of prior-period gas costs is simpler: first, the transaction's gas limit is multiplied by the transaction's gas price. Then the maximum gas cost is added to the total value transmitted from the sender to the recipient.
如何交易符合上面所说的所有要求,那么我们进行下面步骤。
How the deal meets all the above requirements, then we take the next step.
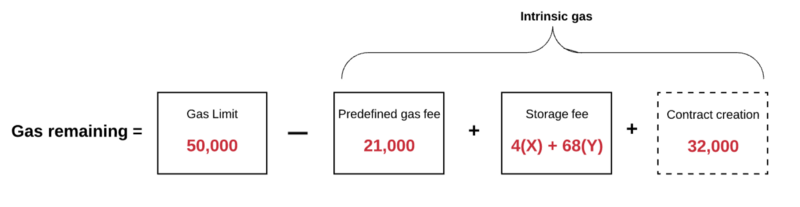
第一步,我们从发送者的余额中扣除执行的前期费用,并为当前交易将发送者账户中的nonce增加1.此时,我们可以计算剩余的gas,将交易的总gas减去使用的intrinsic gas。
As a first step, we deduct the forward cost of implementation from the sender's balance and add nonce to the sender's account by 1 for the current transaction, we can calculate the rest of the gas by subtracting the total of the transaction from the intrinsic gas used.
第二步,开始执行交易。在交易执行的整个过程中,以太坊保持跟踪“子状态”。子状态是记录在交易中生成的信息的一种方式,当交易完成时会立即需要这些信息。具体来说,它包含:
Step two, start the transaction. Throughout the course of the transaction, track the “sub-state” with the Taiwan. The sub-state is a way of recording the information generated in the transaction, which is needed immediately when the transaction is completed. Specifically, it contains:
自毁集:在交易完成之后会被丢弃的账户集(如果存在的话)
Self-destruct collection: A collection of accounts that will be discarded after the transaction has been completed (if any)
日志系列:虚拟机的代码执行的归档和可检索的检查点
Log series: archive and searchable checkpoints executed by the code of the virtual machine
退款余额:交易完成之后需要退还给发送账户的总额。回忆一下我们之前提到的以太坊中的存储需要付费,发送者要是清理了内存就会有退款。以太坊使用退款计数进行跟踪退款余额。退款计数从0开始并且每当合约删除了一些存储中的东西都会进行增加。
Refund balance: The total amount that will have to be returned to the sender account after the transaction has been completed. Remember what we mentioned earlier about the cost of storage in Etheria, if the sender cleans up the memory, there will be a refund. The refund balance will be tracked using refunds. Refunds will start at 0 and increase whenever the contract removes some of the stored items.
第三步,交易所需的各种计算开始被处理。
The third step is that the various calculations required for the transaction are beginning to be processed.
当交易所需的步骤全部处理完成,并假设没有无效状态,通过确定退还给发送者的未使用的gas量,最终的状态也被确定。除了未使用的gas,发送者还会得到上面所说的“退款余额”中退还的一些津贴。
In addition to unused gas, the sender will receive some of the benefits refunded from the “refund balance” referred to above.
一旦发送者得到退款之后:
Once the sender has received a refund:
gas的Ether就会矿工
Ethel of Gas will be a miner.
交易使用的gas会被添加到区块的gas计数中(计数一直记录当前区块中所有交易使用的gas总量,这对于验证区块时是非常有用的)
Gas used in transactions is added to the gas count of blocks (the total number of gas used in all transactions in the current block is always recorded, which is very useful in validating blocks)
所有在自毁集中的账户(如果存在的话)都会被删除
All accounts in self-destruct concentration (if they exist) will be deleted.
最后,我们就有了一个新的状态以及交易创建的一系列日志。
Finally, we have a new state and a series of logbooks created by the transaction.
现在我们已经介绍了交易执行的基本知识,让我们再看看合约创建交易和消息通信的一些区别。
Now that we have described the basics of transaction execution, let us look at some of the differences between contract creation transactions and messaging.
合约创建(Contract creation)
Contract creation
回忆一下在以太坊中,有两种账户类型:合约账户和外部拥有账户。当我们说一个交易是“合约创建”,是指交易的目的是创建一个新的合约账户。
Remember, in Etheria, there are two types of accounts: contractual accounts and externally owned accounts. When we say a transaction is “contract creation”, it means that the purpose of the transaction is to create a new contractual account.
为了创建一个新的合约账户,我们使用一个特殊的公式来声明新账户的地址。然后我们使用下面的方法来初始化一个账户:
In order to create a new contractual account, we use a special formula to declare the address of the new account. We then use the following method to initialize an account:
设置nonce为0
Set nonce to 0
如果发送者通过交易发送了一定量的Ether作为value,那么设置账户的余额为value
If the sender sends a certain amount of Ethan as value through the transaction, then the balance of the set account is value
将存储设置为0
Set storage to zero
设置合约的codeHash为一个空字符串的Hash值
Set a codeHash for an empty string
一旦我们完成了账户的初始化,使用交易发送过来的init code(查看”交易和信息”章节来复习一下init code),实际上就创造了一个账户。init code的执行过程是各种各样的。取决于合约的构造器,可能是更新账户的存储,也可能是创建另一个合约账户,或者发起另一个消息通信等等。
Once we have completed the initialization of the accounts, the init code sent by the transaction is used to review the init code, which actually creates an account. The implementation of the init code is varied. Depending on the builder of the contract, it may be to update the account, or to create another contract account, or to launch another message, etc.
当初始化合约的代码被执行之后,会使用gas。交易不允许使用的gas超过剩余gas。如果它使用的gas超过剩余gas,那么就会发生gas不足异(OOG)常并退出。如果一个交易由于gas不足异常而退出,那么状态会立刻恢复到交易前的一个点。发送者也不会获得在gas用完之前所花费的gas。
When the initialised contract code is implemented, the gas is used. The transaction is not allowed to use the gas more than the remaining gas. If it uses the gas more than the remaining gas, there is a dissimilar (OOG) routine and exit. If a transaction exits because the gas is not enough, the status immediately reverts to a pre-trading point. The sender will not get the gas that was spent before the gas ran out.
不过,如果发送者随着交易发送了Ether,即使合约创建失败Ether也会被退回来。
If, however, the sender sends Ether with the transaction, even if the contract failed, then Ether will be returned.
如果初始化代码成功的执行完成,最后的合约创建的花费会被支付。这些是存储成本,与创建的合约代码大小成正比(再一次,没有免费的午餐)。如果没有足够的剩余gas来支付最后的花费,那么交易就会再次宣布gas不足异常并中断退出。
If the initialization code is successfully implemented, the costs of the final contract creation are paid. These are storage costs, which are proportional to the size of the contract code created (and again, there is no free lunch). If there is not enough gas left to cover the final cost, then the transaction will declare the gas abnormality and suspend its exit.
如果所有的都正常进行没有任何异常出现,那么任何剩余的未使用gas都会被退回给原始的交易发送者,现在改变的状态才被允许永久保存。
If all were to proceed normally without any anomalies, any remaining unused Gas would be returned to the original sender of the transaction and the changed state would now be allowed to remain permanently.
消息通信(Message calls)
Message calls
消息通信的执行与合约创建比较类似,只不过有一点点区别。
The implementation of messages is similar to the creation of contracts, although there is a slight difference.
由于没有新账户被创建,所以消息通信的执行不包含任何的init code。不过,它可以包含输入数据,如果交易发送者提供了此数据的话。一旦执行,消息通信同样会有一个额外的组件来包含输出数据,如果后续执行需要此数据的话就组件就会被使用。
Since no new account has been created, the message message execution does not contain any init code. However, it can contain input data if the sender of the transaction provides this data. Once implemented, the message communication will also have an additional component to include output data, which will be used if the data is needed for follow-up implementation.
就像合约创建一样,如果消息通信执行退出是因为gas不足或交易无效(例如栈溢出,无效跳转目的地或无效指令),那么已使用的gas是不会被退回给原始触发者的。相反,所有剩余的未使用gas也会被消耗掉,并且状态会被立刻重置为余额转移之前的那个点。
As with the creation of the contract, if the message exits because the gas is inadequate or the transaction is not valid (e.g., spilling out, ineffectual jumping destination or invalid instructions), the used gas will not be returned to the original trigger. On the contrary, all remaining unused gass will also be consumed, and the status will be reset immediately to the point before the balance is transferred.
没有任何方法停止或恢复交易的执行而不让系统消耗你提供的所有gas,直到最新的以太坊更新。例如,假设你编写了一个合约,当调用者没有授权来执行这些交易的时候抛出一个错误。在以太坊的前一个版本中,剩余的gas也会被消耗掉,并且没有任何gas退回给发送者。
There is no way to stop or resume the transaction without allowing the system to consume all the gass that you provide until the latest Etheria update. For example, assuming you have a contract, a mistake is made when the caller is not authorized to execute the transaction. In the previous version of Ether, the rest of the gas will also be consumed, and no gas will be returned to the sender.
但是拜占庭更新包括了一个新的“恢复”代码,允许合约停止执行并且恢复状态改变而不消耗剩余的gas,此代码还拥有返回交易失败原因的能力。如果一个交易是由于恢复而退出,那么未使用的gas就会被返回给发送者。
The Byzantine update, however, includes a new “recover” code that allows contracts to be suspended and restored without depleting the rest of the gas, which also has the ability to return to the cause of the failure of the transaction. If a transaction exits as a result of recovery, the unused gas will be returned to the sender.
执行模式
Implementation Mode
到目前为止,我们了解了从开始到结束执行的交易必须经历的一系列的步骤。现在,我们来看看交易究竟是如何在虚拟机(VM)中执行的。
So far, we have learned a series of steps that must be taken from the beginning to the end of the transaction. Now, let's see how the deal is carried out in the VM.
协议实际操作交易处理的部分是以太坊自己的虚拟机,称之为以太坊虚拟机(EVM)。
The actual transaction processing part of the agreement is the Taipan's own virtual machine, known as the Etheria Virtual Machine (EVM).
像之前定义的那样,EVM是图灵完备虚拟机器。EVM存在而典型图灵完备机器不存在的唯一限制就是EVM本质上是被gas束缚。因此,可以完成的计算总量本质上是被提供的gas总量限制的。
As previously defined, EVM is a complete virtual machine in Turing. The only limitation that EVM exists, and the typical Turing machine does not exist, is that EVM is essentially tied to Gas. So, the total amount that can be calculated is essentially limited by the amount of gas supplied.
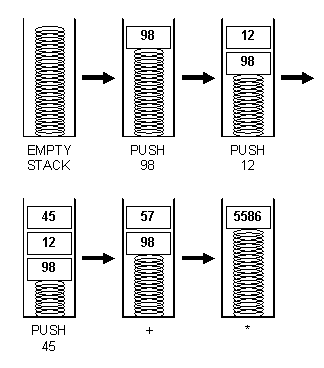
此外,EVM具有基于堆栈的架构。堆栈机器 就是使用后进先出来保存临时值的计算机。
In addition, EVM has a stack-based structure. A stacking machine is a computer that uses back-to-back to save temporary values.
EVM中每个堆栈项的大小为256位,堆栈有一个最大的大小,为1024位。
The size of each stack in EVM is 256 and the size of the stack is one of the largest, 1024.
EVM有内存,项目按照可寻址字节数组来存储。内存是易失性的,也就是数据是不持久的。
EVM has memory, which is stored on a searchable byte array. Memory is fragile, i.e. data are not sustainable.
EVM也有一个存储器。不像内存,存储器是非易失性的,并作为系统状态的一部分进行维护。EVM分开保存程序代码,在虚拟ROM 中只能通过特殊指令来访问。这样的话,EVM就与典型的冯·诺依曼架构 不同,此架构将程序的代码存储在内存或存储器中。
EVM also has a memory. Unlike memory, the memory is non-lossive and is maintained as part of the system's state. EVM separates the program code, which can only be accessed by special commands in virtual ROM. In this case, EVM differs from the typical von Neuman structure, which stores the program code in the memory or memory.
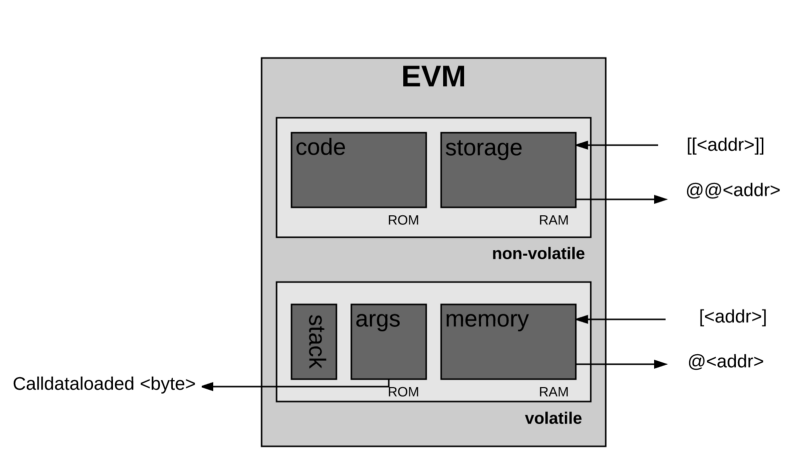
EVM同样有属于它自己的语言:“EVM字节码”,当一个程序员比如你或我写一个在以太坊上运行的智能合约时,我们通常都是用高级语言例如Solidity来编写代码。然后我们可以将它编译成EVM可以理解的EVM字节码。
The EVM also has its own language: the EVM byte code. When a programmer, like you or me, writes a smart contract running on the Ether, we usually write the code in advanced languages, such as Solity. Then we can translate it into the EVM byte code that EVM can understand.
好了,现在来说执行。
Well, let's talk about execution now.
在执行特定的计算之前,处理器会确定下面所说的信息是有效和是否可获取:
Before performing a particular calculation, the processor determines whether the information described below is valid and accessible:
系统状态
System Status
用于计算的剩余gas
Surplus gas for calculation
拥有执行代码的账户地址
Account address with executable code
原始触发此次执行的交易发送者的地址
Address of the original sender of the transaction triggering this execution
触发代码执行的账户地址(可能与原始发送者不同)
Account address for trigger code execution (possibly different from the original sender)
触发此次执行的交易gas价格
Gas price triggering this execution.
此次执行的输入数据
Enter data for this execution
Value(单位为Wei)作为当前执行的一部分传递给该账户
Value (unit Wei) to the account as part of the current execution
待执行的机器码
Machine code to be executed
当前区块的区块头
A block header for the current block
当前消息通信或合约创建堆栈的深度
The depth of the current message or contract to create a stack
执行刚开始时,内存和堆栈都是空的,程序计数器为0.
At the start of the execution, both the memory and the stack were empty and the program counter was 0.
然后EVM开始递归的执行交易,为每个循环计算系统状态和机器状态。系统状态也就是以太坊的全局状态(global state)。机器状态包含:
The system state is the global state of the Etherm. The machine state consists of:
可获取的gas
Available Gas
程序计数器
Program counter
内存的内容
Memory Contents
内存中字的活跃数
Active number of words in memory
堆栈的内容
The contents of the stack
堆栈中的项从系列的最左边被删除或者添加。
Items in the stack are deleted or added from the leftmost side of the series.
每个循环,剩余的gas都会被减少相应的量,程序计数器也会增加。
For each cycle, the remaining gas will be reduced and the programme counter will be increased.
在每个循环的结束,都有三种可能性:
At the end of each cycle, there are three possibilities:
机器到达异常状态(例如 gas不足,无效指令,堆栈项不足,堆栈项会溢出1024.无效的JUMP/JUMPI目的地等等)因此停止,并丢弃任何的更改
Machines reached an abnormal state (e.g. lack of gas, invalid instructions, insufficient stacking items, overflow of 1024. invalid JUMP/JUMPI destinations, etc.) and therefore stopped and discarded any changes
进入后续处理下一个循环
Entering the next cycle of follow-up
机器到达了受控停止(到达执行过程的终点)
The machine has reached the controlled stop (at the end of the execution process)
假设执行没有遇到异常状态,达到一个“可控的”或正常的停止,机器就会产生一个合成状态,执行之后的剩余gas、产生的子状态、以及组合输出。
Assuming that there is no abnormal state of execution, reaching a “controllable” or normal stoppage, the machine produces a synthetic state with the remaining gas after execution, the resulting sub-state, and the combined output.
呼。我们终于过了一遍以太坊最难的部分了。如果你不能完全理解这个部分,也没关系。除非你在理解非常深层次的东西,否则你真的没有必要去理解执行的每个细节。
Whoo. We've finally passed the hardest part of Ether. It doesn't matter if you don't fully understand this part. Unless you understand very deeply, you really don't have to understand every detail of implementation.
一个块是如何完成的?
How's a piece done?
最后,让我们看看一个包含许多交易的块是如何完成的。
And finally, let's see how a block of many transactions is done.
当我们说“完成”,取决于此块是新的还是已存在的,可以指两个不同的事情。如果是个新块,就是指挖这个块所需的处理。如果是已存在的块,就是指验证此块的处理。不论哪种情况,一个块的“完成”都有4个要求:
When we say "finished," it depends on whether the block is new or existing, and it can mean two different things. If it is a new block, it means the treatment needed to dig it. If it is an existing block, it means the treatment to verify it. In either case, there are four requirements for a "finished" block:
1)验证(或者,如果是挖矿的话,就是确定)ommers
1) Validation (or, in the case of mining, confirmation) ommers
在区块头中的每个ommer都必须是有效的头并且必须在当前块的6代之内
Every mmer in a block must be an effective head and within six generations of the current block.
2)验证(或者,如果是挖矿的话,就是确定)交易
2) Validation (or, in the case of mining, determination) of the transaction
区块中的gasUsed数量必须与区块中所列交易使用的累积gas量相等。(回忆一下,当执行一个交易的时候,我们会跟踪区块的gas计数器,也就跟踪了区块中所有交易使用的gas总数量)
The number of gasUsed in a block must be equal to the cumulative amount of gas used in the transactions listed in the block. (Remember, when a transaction is carried out, we track the gas counter in the block, and we track the total number of gass used in all transactions in the block.)
3)申请奖励(只有挖矿时)
3) Applying for an incentive (only when mining is mined)
受益人的地址会因为挖矿而获得5Ether(在以太坊EIP-649 提案中,5ETH很快将会被减少为3ETH)。另外,对于每个ommer,当前块的受益人会获得额外的1/32当前块奖励金的奖励。最近,每个ommer区块的受益人能够得到一定量的奖励(有个特殊公式可以进行计算)。
The address of the beneficiary will be 5 Ether for mining (in Ether's EIP-649 proposal, 5ETH will soon be reduced to 3ETH). In addition, for each omer, the beneficiary of the current block will receive an additional 1/32 current incentive. Recently, the beneficiary of each ommer block will receive a certain amount of reward (a special formula can be calculated).
4)校验(或者,如果是挖矿的话,就是计算一个有效的)状态和nonce
4) Verify (or, in the case of mining, calculate a valid) state and nence
确保所有的交易和改变的结果状态都被应用了,然后在区块奖励被应用于最终交易结果状态之后定义一个新块为状态。通过检查最终状态与存储在头中的状态树来进行验证。
Ensure that all transactions and changed result states are applied, and then a new block is defined as a state after block incentives are applied to the final result state. Validation is done by checking the end state and the state tree stored in the head.
工作量证明挖矿
Workload certified mining
在“区块”这个章节简短的说明了一下区块难度这个概念。给予区块难度意义的算法叫做工作量证明(PoW)。
The concept of block difficulty is briefly described in the block section.
以太坊的工作量证明算法称之为“Ethash” (之前叫做Dagger-Hashimoto)。
It's called “Ethash” (formerly Dagger-Hashimoto) based on the Taiku workload proof algorithm.
算法正式定义为:
The algorithm is formally defined as:
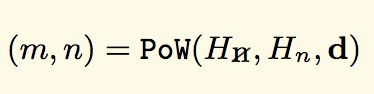
m代表的是mixHash,n代表的是nonce,Hn代表的是新区块的头(不包含需要计算的nonce和mixHash),Hn是区块头的nonce,d是DAG ,就是一个大数据集。
m For mixHash, n for nence, Hn for the head of the new block (not including nence and mixHash to be counted), Hn for nonce, d for DAG, is a large data set.
在”区块”章节,我们讨论了存在于区块头中的多项。其中两项叫做mixHash和nonce。也许你会回忆起:
In the block section, we discuss the many that exist in the block. Two of them are called "mixHash" and "nonce." Perhaps you remember:
mixHash:一个Hash值,当与nonce组合时,证明此区块已经执行了足够的计算
MixHash: a Hash value which, when combined with nance, proves that the block has performed sufficient calculations
nonce:一个Hash值,当与mixHash组合时,证明此区块已经执行了足够的计算
Nonce: a Hash value which, when combined with MixHash, proves that the block has performed sufficient calculations
PoW函数就是用来估算这两项的。
The Pow function is used to estimate both.
mixHash和nonce到底是如何使用PoW函数来计算出来的有点复杂,如果深入了解的话,我们可以另写一篇文章来讲解了。但是在一个高层面上,它大致就是这样计算的:
It's a little complicated how the mixHash and nence use the PoW function, and if we know it in depth, we can write another article to explain it. But at a high level, it's basically this way:
会为每个区块计算一个”种子”。每个“时期”的种子都不一样,每个时期是30.000个区块长度。对于第一时期,种子就是32位0的hash值。对于后续的每个时期,种子就是前一个种子hash值的hash值。使用这个种子,节点可以计算一个伪随机“缓存”。
For each block, a “seed” is calculated. Each “period” of seeds is different, with 30,000 block lengths. For the first period, the seed is a 32-bit hash value. For each subsequent period, the seed is the hash value of the previous hash value. With this torrent, the node can calculate a pseudo-random cache.
这个缓存是非常有用的,因为它可以使“轻节点”的概念变成现实,轻节点概念在这篇文章的前面讨论过。轻节点的目的就是让某个节点有能力高效的校验交易而用不着存储整个区块链的数据集。一个轻节点可以仅基于缓存来校验一个交易的有效性,因为缓存可以重新生成需要校验的特定块。
This cache is very useful because it can make the concept of a “light node” a reality, as discussed earlier in this article. The purpose of a light node is to enable a node to verify transactions efficiently without storing data sets of entire block chains. A light node can verify the validity of a transaction based solely on a cache, because a cache can recreate a specific block that needs to be verified.
使用这个缓存,节点可以生成DAG“数据集”,数据集中的每项取决于缓存中少量伪随机选择项。为了成为矿工,你需要要生成全数据集,所有全客户端和矿工都保存这个数据集,并且这个数据集随着时间线性增长。
With this cache, nodes generate the DAG data set, each of which depends on a small number of pseudo-random selections in the cache. To be a miner, you need to generate a full data set, which is kept by all clients and miners, and which grows linearly over time.
然后矿工可以随机抽取数据集中的部分并将它们放入一个数学函数中Hash出一个”mixHash”。矿工会重复生成mixHash直到输出的值小于想要的目标值nonce。当输出的值符合这个条件的时候,nonce就被认为是有效的,然后区块就被添加到链中。
The miners can then randomly extract parts of the data set and place them in a mathematical function Hash out of a'mixHash '. The union repeats the production of mixHash until the value of the output is less than the desired target value nence. When the value of the output meets this condition, nonce is considered valid and the block is added to the chain.
挖矿作为安全机制
Mining as a security mechanism
总的来说,PoW的目的就是以加密安全的方式证明生成的一些输出(也就是nonce)是经过了一定量的计算的。因为除了列举所有的可能性,没有更好的其他方法来找到一个低于要求阈值的nonce。
In general, PoW aims to demonstrate that some of the output generated (i.e., nence) has been calculated in a secure way by encryption. There is no better way to find a nonce below the required threshold than to list all the possibilities.
重复应用Hash函数的输出均匀分布,所以我们可以确保,在平均值上,找到满足要求的nonce所需时间取决于难度阈值。难度系数越大,所需时间越长。这样的话,PoW算法就给予难度这个概念的意义了:用来加强区块链的安全。
Repeats the output of the Hash function are evenly distributed, so we can ensure that, on average, the time it takes to find a nonne that meets the requirement depends on the difficulty threshold. The greater the difficulty factor, the longer it takes. In this case, the PoW algorithm gives meaning to the notion of difficulty: it is used to enhance the security of the block chain.
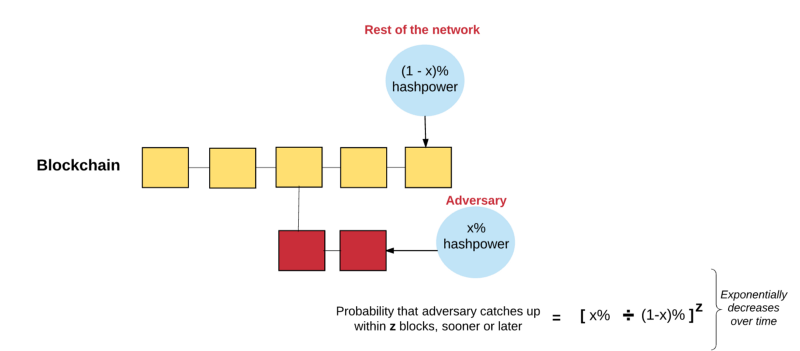
我们所说的区块链的安全又是什么意思?这非常简单:我们想要创造一个每个人都信任的区块链。像我们之前在这篇文章中讨论的那样,如果存在超过1条以上的链,用户的信任就会消失,因为他们没有能力合理的确认哪条链才是“有效的”。为了让一群用户接受存储在区块链中的潜在状态,我们需要有一群人信任的一个权威区块链。
What do we mean by the security of the block chain? It's very simple: we want to create a chain of blocks that everyone trusts. As we discussed earlier in this article, if more than one chain exists, the trust of users will disappear, because they cannot reasonably identify which chain is “effective.” In order for a group of users to accept the potential state of storage in the block chain, we need a chain of authoritative blocks that a group of people trusts.
这完完全全就是Pow算法所做的事情:它确保特定的区块链直到未来都一直保持着权威性,让攻击者创造一个新区块来重写某个历史部分(例如清除一个交易或者创建一个假的交易)或者保持一个分叉变得非常困难。
This is exactly what the Pow algorithm does: it ensures that a particular block chain remains authoritative until the future, making it very difficult for the attackers to create a new block to rewrite a historical part (e.g. clear a transaction or create a false one) or to maintain a split.
为了首先让他们的区块被验证,攻击者需要总是比网络上的其他人要更快的解决掉nonce问题,这样网络就会相信他们的链是最重的链(基于我们之前提到的GHOST协议原则)。除非攻击者拥有超过一半的网络挖矿能力(这种场景也被称为大多数51%攻击 ),要不然这基本上是不可能的。
In order for their blocks to be proven first, the attackers need to always solve the nence problem faster than the rest of the network, so that the network believes that their chains are the heaviest (based on the GHOST principles we have mentioned earlier). Unless the attackers have more than half of their network mining capacity (which is also referred to as most 51% of the attacks), this would be virtually impossible.
挖矿作为财富分配机制
Mining as a mechanism for wealth distribution
除了提供一个安全的区块链,PoW同样也是分配财富给那些为提供这个安全而花费自己计算力的人的一种方法。回忆一下,一个矿工挖出一个区块的时候会获得奖励,包括:
In addition to providing a secure chain of blocks, PoW is also a way to distribute wealth to those who spend their computing power to provide this security. Remember, a miner is rewarded when he digs a block, including:
为“获胜”区块提供的5 ether静态区块奖励(马上就会变成3 ether )
5 other static block incentives for "winner" blocks (which will soon become 3 other)
区块中的交易在区块内所消耗的gas
Gas that transactions in blocks consume within blocks
纳入ommers作为区块的一部分的额外奖励
Additional incentives to include ommers as part of blocks
为了保证PoW共识算法机制对安全和财富分配的使用是长期可持续的,以太坊努力灌输这两个特性:
In order to ensure that the use of the PoW Consensus algorithm mechanism for security and distribution of wealth is sustainable in the long term, the Pacific has tried to inculcate these two characteristics:
尽可能的让更多的人可访问。换句话说,人们不需要特殊的或者与众不同的硬件来运行这个算法。这样做的目的是为了让财富分配模式变的尽可能的开放,以便任何人都可以提供一些算力而获得Ether作为回报。
In other words, people do not need special or different hardware to run the algorithm. The aim is to keep wealth distribution patterns as open as possible, so that anyone can provide some measure to get Ethan in return.
降低任何单个节点(或小组)能够创造与其不成比例的利润可能性。任何可以创造不成比例的利润的节点拥有比较大的影响力来决定权威区块链。这是件麻烦的事情,因为这降低了网络的安全性。
Any single node (or group) can create a disproportionate profit potential. Any node that can generate a disproportionate profit has greater influence to determine the chain of authoritative blocks. This is problematic because it reduces the security of the network.
在区块链网络中,一个与上面两个特性有关的一个问题是PoW算法是一个SHA256哈希函数。这种函数的缺点就是它使用特殊的硬件(也被称之为ASCIs)可以更加快速高效的解决nonce问题。
In the block chain network, one of the problems associated with the above two characteristics is that the PoW algorithm is a SHA256 Hashi function. The disadvantage of this function is that it solves the nence problem more quickly and efficiently with special hardware (also known as ASCIs).
为了减轻这个问题,以太坊选择让PoW算法(Ethhash) 提高内存级别难度。意思是此算法被设计为计算出要求的nonce需要大量的内存和带宽。大量内存的需求让电脑平行的使用内存同时计算多个nonce变得极其困难,高带宽的需求让即使是超级电脑同时计算多个nonce也变得十分艰难。这种方式降低了中心化的风险,并为正在进行验证的几点提供了更加公平的竞争环境。
In order to alleviate this problem, the Taiq chose to make the PoW algorithm (Ethhash) more difficult for memory levels. It means that the algorithm was designed to calculate the required amount of memory and bandwidth. The need for large amounts of memory makes it extremely difficult for computers to use multiple nonce in parallel, and the need for high bandwidth makes it very difficult for even supercomputers to calculate multiple nonce at the same time.
有一件值得注意的事情是以太坊正在从PoW共识机制渐渐转换为一个叫做“权益证明(PoS)”的共识算法。这就是一个比较野心的话题了,我们希望可以在未来的文章中探索这个话题。
It is worth noting that the Tails are moving from the PoW Consensus mechanism to a consensus algorithm called PoS. This is a more ambitious topic that we hope will be explored in future articles.
总结
Summary
呼! 你终于坚持到最后了。我希望如此?
You're finally at the end. I hope so.
这篇文章中有很多的地方需要消化。如果需要你阅读好几遍才能理解怎么回事,这完全正常。我个人重复阅读了好几次以太坊黄皮书,白皮书,以及代码的不同部分才渐渐明白是怎么回事。
There are a lot of areas in this article that need to be digested. It's perfectly normal if you have to read it several times in order to understand what's going on. I read it several times in taupe, white papers, and different parts of the code.
无论如何,我希望你觉得这篇文章对你有帮助。如果你发现了任何的错误或失误,我很乐意你给我写个私人消息或者直接在评论区评论(我保证我会查看所有评论)。
Anyway, I want you to think that this article will help you. If you find any mistakes or mistakes, I'd be happy to write me a personal message or comment directly in the comment area (I promise I'll look at all the comments).
记住,我是个人类(对,这是真的),我会犯错误。为了社区的利益,我花时间免费写了这篇文章。所以请你在反馈时不要带着没必要的攻击性,尽量是建设性的反馈。
Remember, I'm a human being, and I make mistakes. For the benefit of the community, I write this article free of charge. So don't try to be as aggressive and constructive as possible in your feedback.
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群



















发表评论