1. 引言
从20世纪90年代开始,许多国家和地区已经应用可追溯系统进行食品以及农产品质量安全管理。在市场经济高度发达的美国,农产品可追溯系统主要是企业自愿建立,政府主要起到推动和促进作用。美国的行业协会和企业建立了自愿性可追溯系统。由70多个协会、组织和100余名畜牧兽医专业人员组成了家畜开发标识小组(USAIP),共同参与制定并建立家畜标识与可追溯工作计划,其目的是在发现外来疫病的情况下,能够在48小时内确定所有涉及与其有直接接触的企业。2003年5月FDA公布了《食品安全跟踪条例》,要求所有涉及食品运输、配送和进口的企业要建立并保全相关食品流通的全过程记录。
Since the 1990s, many countries and regions have applied retroactive systems for the safe management of food and agricultural products. In the United States, where the market economy is highly developed, the traceability system for agricultural products is largely voluntary, with the Government acting as a catalyst and catalyst. Industry associations and businesses in the United States have established a voluntary traceability system.
而我国对食品溯源系统也在不断地完善,2016年10月,阿里健康联合天猫医药共同启动“滋补中国”品牌战略,并宣布建立“滋补中国追溯体系”,实现对滋补品“一品一码”的追溯。借助阿里健康“码上放心”平台,可以实现对相关滋补品的溯源,相当于滋补品都有了“身份证”。虽然现在溯源越来越被看重但是传统的溯源方式还是存在很多问题未解决,将食品信息集中存储在一个中心数据库里有被人为篡改的风险,造成消费者或者监管者对食品信息的信息不对称从而带来很多危害,而区块链技术的分布式存储的结构形成了去中心化的数据存储 [1] ,极大的保证了信息对称性。
My country is also improving its food traceability system, and in October 2016 Ali’s Healthy United Skycat Medicines jointly launched a brand-new strategy to “get China” and announced the creation of a “get China back together” system to provide a “one-size-fits-all” retroactive response to the supplement. Through the Ali’s health “code-by-code” platform, it is possible to trace the supplement, which is equivalent to a “identity card” for the supplement. While it is now increasingly valued, there are many unresolved problems with traditional traceability, with centralized food information stored in a central database at risk of being tampered with, causing many hazards to consumers or regulators asymmetrics of food information, while the distributional structure of block-chain technology has created decentralized data storage [1], which provides a great guarantee of symmetry of information.
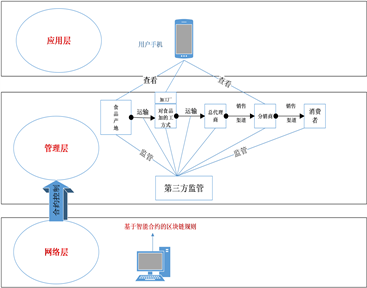
本文将区块链与食品溯源相结合构建一个基于区块链技术的溯源系统,其核心是三层架构,能够解决现有溯源系统的部分痛点。该系统架构分为应用层、管理层、网络层三层,实现食品从采摘、加工以及销售过程都可从手机App查询进而达到有效溯源。
This paper combines block chains with food traceability to construct a system of traceability based on block chain technology, the core of which is a three-storey structure capable of addressing some of the pains of the existing traceability system. The system is structured into three layers: application, management, network, and the process of extracting, processing, and selling food can be accessed from a mobile phone app to an effective traceability.
2. 区块链
2.1. 区块链的意义
区块链技术是密码学、计算机科学、经济学等多个学科发展到一定阶段后的产物,有效融合了多个学科的杰出成果。区块链技术的出现为解决人类社会的信任问题提供了有力工具,进而将人类社会带入群智时代。
Block chain technology is the product of a number of disciplines, such as cryptology, computer science, and economics, that have evolved to a certain stage, effectively integrating outstanding results from multiple disciplines. The emergence of block chain technology provides a powerful tool for solving the problems of trust in human society, thus bringing human society into the age of intelligence.
区块链系统本身能产生信用,这种具有信用的产品不是来自第三方,而是来自程序(算法),因为区块链记录信息的产生需要全网络节点确认,而一旦生成将永久记录,无法篡改。互联网的底层协议是TCP/IP协议,实现了信息的低成本高效率传播;区块链可认为是一种新的底层技术,建立了新的信用体系。区块链取代了目前互联网对中心服务器的依赖,使所有数据信息都被记录在一个云系统之上,理论上实现了数据传输中的数据自我证明,从深远意义上讲,这超越了传统和常规意义上需要依赖第三方的信息验证模式,降低了建立全球信用体系的成本。
The block chain system itself generates credit, not from a third party, but from a process (arithmetic), because the creation of information in the block chain records requires full network nodes to confirm, and once generated it will be permanent, and cannot be tampered with. The bottom protocol on the Internet is the TCP/IP protocol, which achieves cost-effective and efficient dissemination of information; the block chain can be seen as a new bottom technology, creating a new credit system. The block chain replaces the current reliance on central servers on the Internet, allowing all data information to be recorded on a cloud system, theoretical self-proven data in data transmission, which in far-reaching terms goes beyond the traditional and conventional information verification model that relies on third parties and reduces the cost of establishing a global credit system.
区块链还创造了一种新的价值交互方式基于“弱中心化” [2] ,但这并非意味着传统社会里各种“中心”的完全消失,未来区块链将出现大量的“多中心”体系,以联盟链、私有链或混合链为主,区块链将会进一步提高“中心”的运行效率,并降低其相当一部分成本。
Block chains have also created a new value interface based on “weak centralization” [2], but this does not mean that the various “centres” in traditional societies have disappeared altogether, that there will be a large number of “centres” in the future, and that the “centres” will be more efficient and reduce a significant portion of their costs, depending on the alliance chain, the private chain or the mixed chain.
区块链是一种由多方共同维护,以块链结构存储数据,使用密码学保证传输和访问安全,能够实现数据一致存储,无法篡改,无法抵赖的技术体系。这种技术给世界带来了无限的遐想空间,全球对区块链的关注热度持续升温,全球主要经济体从国家战略层面开始对区块链技术及发展趋势进行研究。
Block chains are technological systems that are jointly maintained by multiple actors, store data in a chain structure, use cryptography to secure transmission and access, and are capable of achieving consistent data storage that cannot be tampered with or denied. This technology provides the world with unlimited room for imagination, global interest in block chains continues to warm up, and major global economies begin to conduct research on block chain technologies and trends at the national strategic level.
可以这样说,第一次工业革命是蒸汽机的发明为标志,第二次工业革命是以电力的产生,第三次工业革命是电脑与互联网信息技术的出现,那么第四次工业革命将是区块链技术的诞生。
It could be argued that the first industrial revolution was marked by the invention of a steam engine, the second industrial revolution by the generation of electricity, and the third industrial revolution by the advent of computer and Internet information technology, and that the fourth industrial revolution would be the birth of block-chain technology.
2.2. 区块链特点
基于区块链的系统和以往的其他系统有很多的不同之处,以区块链为核心的有以下几大特点:
There are many differences in the systems based on the block chain and other systems of the past, with the following main features at the heart of the block chain:
1) 分布式的(Distributed):区块链没有中心节点,数据分布式的存储在各个节点上,即使绝大部分节点毁灭了,只要还有一个节点存在就可以重新建立并且还原区块链数据。
1) Distributed (Distributed): The block chain has no central nodes and the data distribution is stored on all nodes, even if most nodes are destroyed, so long as there is one node, it can be recreated and the chain of blocks restored.
2) 自治的(Autonomous):区块链是一种去中心化的、自治的体系 [3] ,所有节点是对等的,每个节点可以自由的加入或者离开但不会影响整个区块链系统,并且当系统运作起来可自行产生区块并同步数据,无需人工参与。
2) Autonomous: The block chain is a decentralised, autonomous system[3], all nodes are reciprocal, each node can be freely joined or left without affecting the entire block chain system, and when the system functions, it can generate blocks and synchronize data without manual involvement.
3) 按照合约执行(Contractual):区块链是完全按照合约执行的,各个节点都有运行规则,一旦不符合规则就会被抛弃,其中最重要的便是智能合约,智能合约是一种可程序化的合同条款、规则或规定。
3) Performance under contract (Contractual): The block chain is performed in full compliance with the contract, with operating rules at all nodes, which are abandoned if they do not comply, the most important of which is an intelligent contract, which is a procedural contractual term, rule or provision.
4) 可追溯(Trackable):区块链中的数据是公开透明的,不能被篡改 [4] ,并且相关区块之间有一定的关联性,因而和容易被追溯。
4) Retroactivity: The data in the block chain are open and transparent, cannot be tampered with[4] and there is some correlation between the blocks in question, which makes them easily retraceable.
若我们把每一个区块看作是一个账本上面记录着所有的交易记录,那不同区块之间的联系也可以看作不同的交易,则其工作的原理如图1所示。
If we see each block as a book of records of all transactions, then the link between the different blocks can also be considered a different transaction, as shown in figure 1 .
区块链(blockchain)是由多个区块链链接而成的连表结构,除了首区块(“创世区块”)之外,每个区块都由前一个区块的输出脚本控制,如图1所示每个区块都可以看成一个账本上面都有对应的交易记录a, b, c...n,每个区块都由前一区块的输出脚本与后一个区块的输入脚本联系起来,此时我们可以形象的把输出脚本和输入脚本看作一把锁和钥匙之间的关系,只有正确的钥匙才能打开正确的锁,以区块1,区块2为例如果区块2输入脚本是区块1的正确的钥匙那么区块1,区块2之间的交易才有效,否则交易无效,交易有效之后交易b也会包含一部分交易a的信息,这时候我们就可以根据区块2溯源到区块1。
The block chain (blockchain) is a table structure linked to multiple block chains, with each block controlled by an output script of the former block, such as . Each block can be seen as having a corresponding transaction record on the book, a _self' . Each block can be seen as having a proper link to the trading block, b, c.n. Each block can be linked by an output script from the previous block to a later block.
近几年区块链技术从1.0时代发展到2.0时代再到正在到来的3.0时代,其共识机制扮演着不可或缺的角色,整个区块链网络是靠区块之间的节点通过共识机制维持着稳定。现在主流的共识算法有以下几种 [5] :
2) POS算法:股权证明算法,是根据参与者持有整个系统的代币的数量和时间来确定记账权的算法。
本文溯源系统为长远打算选取的是根据POS改进得到的DPOS算法即股权授权算法,是在参与者里通过类似居委会选举制度,选举一部分人为代表人进行投票确定记账权,优化了POS算法中可能出现的中心化现象。
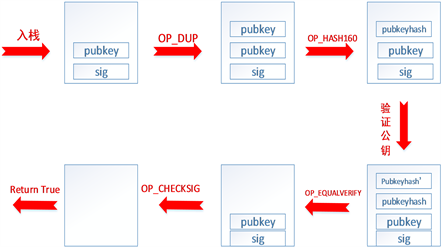
当区块内的信息状态要发生转移时,为保证数据信息的安全性与真实性,区块链节点之间在共识机制的依托之下需要对区块信息进行签名,而交易方必须拿到对应的公钥才能解密才能看到真实的数据信息,验证过程由脚本语言控制其执行的原理如图2所示。
In order to ensure the security and authenticity of data information when the information state within a block is to be transferred, signature of block information between block chain nodes is required under the mechanism of consensus, and the trader must have the corresponding public key in order to decipher the true data information. The principle that the authentication process is controlled by script language is as
Figure 2. Script execution diagram
图2. 脚本执行图
所以脚本执行过程如图2所示第一步先将私钥公钥依次入栈,在通过OP_DUP命令复制栈顶元素,然后通过OP_HASH160命令对公钥进行hash算法加密,此过程保证了公钥的安全性,防止恶性攻击偷取公钥。
So the script execution process is , which ensures the security of public keys and prevents malicious attacks from stealing them.
公钥加密后只有交易双方知道,所以当发起交易者想要进行交易时需要交易的另一方提供同样的公钥,因此第四步
Once the public key is encrypted, only the parties to the transaction know that the same public key is required from the other party to the transaction when the initiating party wishes to carry out the transaction, so step four
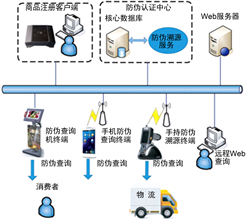
食品溯源系统在物联网的技术支撑下被越来越多的企业所应用,传统的溯源体系现在主要有利用二维码或者RFID技术给食品印上“身份证”,用户可以在手机APP上查询食品的生命周期信息做到全面的了解,做到消费更透明,同时食品追溯体系的建立,当发生质量事故时能够提出恰当的应对措施,降低消费者的损失,使得消费者的利益能够得到保障。传统的溯源体系如图3所示。
Food traceability systems are being used by an increasing number of enterprises, supported by technology for networking, and traditional traceability systems are now mainly “identity cards” printed on food using two-dimensional codes or RFID technologies. Users can access information on the life cycle of food on mobile phones for comprehensive understanding and transparency of consumption, while food traceability systems can be set up to provide appropriate responses in the event of a quality accident to reduce consumer losses and safeguard consumer interests. Traditional traceability systems such as
为解决基于传统食品溯源系统的缺陷,可以构建基于区块链的食品溯源系统,区块链中可以任意添加或者减少区块而不影响整个系统可以使得系统更具有动态性和实效性,每生成一个区块都由唯一的不可更改的时间戳保证了其不可篡改 [9] 、不可复制性。将各类信息都放在区块链上,其公开透明的数据可以使用户直观的看到,使得消费者对食品,基于以上特点本文设计出如图4所示的基于区块链的溯源系统框架。
To address deficiencies based on traditional food traceability systems, a system of food traceability based on block chains can be constructed in which blocks can be added or reduced at will without compromising the system's dynamic and effectiveness. Each block generated by a single unalterable time stamp guarantees its immutable [9], non-repelicable nature. The transparent data placed on the block chains allows users to visualize the food by allowing consumers to be designed on the basis of the above-mentioned text, as
对于管理层第三方的监管则只需要监管者加入区块链系统并且拿到相应的公钥便能查询,但即便是监管者也是无权、无法篡改信息内容的,也避免了监管者在食品出现质量问题进行食品溯源追责的时候出现徇私舞弊的情况。
针对本文的食品溯源而言,图4里的管理层的每一个环节都是被授权参与者,当被授权的参与者要维护食品的信息文档时,必须需要此参与者的私钥连接网络后,进行数据信息的输入,在进行数字签名。系统要收集一系列的信息,包括但不限于商品当前状态、产品类型、行业标准等。一旦参与者发起了产品转移,通过智能合约对数据进行审核、验证,之后将信息打包录入。被授权的节点在与另一节点进行“交易”时,两节点之间需要达成统一的协议并进行数字签名。数字签名此处采用ECDSA (非对称数字加密)技术,保证了信息不被篡改且两节点之间信息无需公开。当“交易”在区块链网络中被核心层节点公证并进行全网广播之后 [11] ,包含交易信息的区块按照时间戳顺序成为区块链上的最新环节。双方交易信息的加密通过非对称加密完成的,即用私钥加密在用相应的公钥解密,保证了信息无法被恶意篡改,解决了交易过程中的诚信问题。
For the food retrospective sources in this paper, 数据访问




















发表评论