本文檔介紹如何使用Nexus 7000部署LISP IGP協助擴展子網模式(ESM)
This document provides an overview of how to deploy LISP IGP help to expand the network mode (ESM) using Nexus 7000.
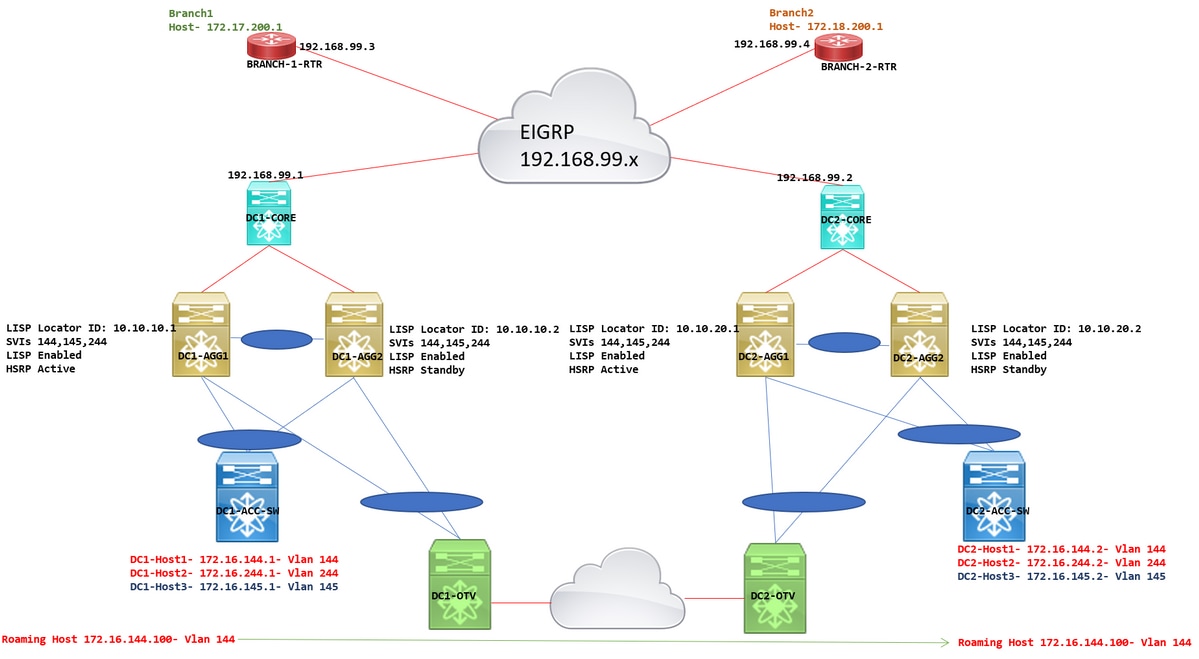
- DC1和DC2是OTV擴展的兩個位置
- Vlan 144、145和244在所有聚合、接入層和OTV交換機上配置
- 這些Vlan的SVI在Agg交換機上配置。SVI 144和244位於VRF租戶1中;SVI 145位於VRF tenant-2中。
- 部署LISP IGP Assist時,SVI不必位於VRF中;此示例使用多個VRF來說明所需的配置更改(在每個相關VRF上下文下);所有SVI都可以位於同一個VRF中,並且仍然可以使用LISP IGP輔助
- HSRP在Vlan144、145和244中配置;在此拓撲中配置了FHRP隔離,這意味著總共4台交換機將運行HSRP,並且兩端將具有活動/備用對。FHRP隔離通過過濾HSRP Hello消息來實現。
- DC1-agg1和DC2-Agg2是vPC對;同樣適用於DC2-Agg1和DC2-Agg2
- LISP配置應用於SVI 144、145和244
- EIGRP鄰居關係是每個VRF從Agg到核心交換機建立的。從每個VRF的Agg交換機到核心交換機運行子介面,並在這些子介面上形成EIGRP鄰居關係。
- 遠端路由器(分支)也是同一個IGP域的一部分。
- 使用LISP IGP Assist時,沒有LISP封裝/解封裝,因此LISP路由必須重新分發到IGP(這裡是EIGRP)。 對於本文檔中描述的此部署模型,分支路由器將不具有任何LISP配置。
- agg,核心交換機是運行8.2(4)NXOS版本的SUP2E、F3/M3的Nexus 7000
- 分支機構路由器是ASR1ks
- 這些Nexus 7000交換機上的另一個VDC中配置了OTV;OTV和LISP必須在不同的VDC上。共用VDC不是選項。
本文中的資訊是根據特定實驗室環境內的裝置所建立。文中使用到的所有裝置皆從已清除(預設)的組態來啟動。如果您的網路正在作用,請確保您已瞭解任何指令可能造成的影響。
The information in this paper is based on a device in a given laboratory environment. All devices used in the text are activated by a cleared (predicted) configuration. If your network is working, make sure you are aware of the implications of any instructions.
Common Configuration on both DC1-Agg1 and DC1-Agg2
feature lisp
vrf context tenant-1 # This example is based on SVI 144 in VRF- tenant-1 and SVI 145 in VRF- tenant-2
ip lisp etr # This is needed to initialize LISP and only etr is needed on a IGP assist mode Environment
lisp instance-id 2 # Instance-ID should be unique per VRF
ip lisp locator-vrf default # Locator Is specified in Default VRF
lisp dynamic-eid VLAN144 # Dynamic EID definition for Vlan 144
database-mapping 172.16.144.0/24 10.10.10.1 priority 50 weight 50 # Database-mapping for 172.16.144.0/24 which is the Vlan 144; IP-> 10.10.10.1 is the Loopback100 IP address(which is the unique IP on DC1-AGG1)
database-mapping 172.16.144.0/24 10.10.10.2 priority 50 weight 50 # Database-mapping for 172.16.144.0/24 which is the Vlan 144; IP-> 10.10.10.2 is the Loopback100 IP address(which is the unique IP on DC1-AGG2)
map-notify-group 239.254.254.254 # Multicast group that will be used by LISP enabled switches to communicate about new EID learns or periodic EID notification messages
no route-export away-dyn-eid # This is a hidden command required to stop advertising any null0 /32 route for a remote host to the IGP
lisp dynamic-eid VLAN244 # Dynamic EID definition for Vlan 244
database-mapping 172.16.244.0/24 10.10.10.1 priority 50 weight 50
database-mapping 172.16.244.0/24 10.10.10.2 priority 50 weight 50
map-notify-group 239.254.254.254
no route-export away-dyn-eid
vrf context tenant-2
ip lisp etr
lisp instance-id 3
ip lisp locator-vrf default
lisp dynamic-eid VLAN145
database-mapping 172.16.145.0/24 10.10.10.1 priority 50 weight 50
database-mapping 172.16.145.0/24 10.10.10.2 priority 50 weight 50
map-notify-group 239.254.254.254
no route-export away-dyn-eid
Configuration on DC1-Agg1
interface Vlan144
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-1
lisp mobility VLAN144
lisp extended-subnet-mode # SVI needs to be in ESM Mode-Extended subnet mode
ip address 172.16.144.250/24
ip pim sparse-mode
hsrp 144
preempt
priority 254
ip 172.16.144.254
interface Vlan145
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-2
lisp mobility VLAN145
lisp extended-subnet-mode
ip address 172.16.145.250/24
ip pim sparse-mode
hsrp 145
preempt
priority 254
ip 172.16.145.254
interface Vlan244
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-1
lisp mobility VLAN244
lisp extended-subnet-mode
ip address 172.16.244.250/24
hsrp 244
preempt
priority 254
ip 172.16.244.254
interface loopback100
ip address 10.10.10.1/32
ip router eigrp 100
ip pim sparse-mode
Configuration on DC1-Agg2
interface Vlan144
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-1
lisp mobility VLAN144
lisp extended-subnet-mode
ip address 172.16.144.251/24
ip pim sparse-mode
hsrp 144
ip 172.16.144.254
interface Vlan145
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-2
lisp mobility VLAN145
lisp extended-subnet-mode
ip address 172.16.145.251/24
ip pim sparse-mode
hsrp 145
ip 172.16.145.254
interface Vlan244
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-1
lisp mobility VLAN244
lisp extended-subnet-mode
no ip redirects
ip address 172.16.244.251/24
hsrp 244
ip 172.16.244.254
interface loopback100
ip address 10.10.10.2/32
ip router eigrp 100
ip pim sparse-mode
#資料庫對映必須這樣提供:在一端,需要指定DC1-Agg1和DC1-Agg2環回IP地址;在DC2-Agg1和DC2-Agg2中,必須建立唯一的環回,並將其放入資料庫對映中。
#Database mapping must be provided as follows: on one end, DC1-Agg1 and DC1-Agg2 need to be assigned to loop back to IP addresses; in DC2-Agg1 and DC2-Agg2, a unique loop must be created and placed in the database.
#在IGP輔助模式下,如果使用configuration-> "ip lisp itr-etr",將導致為未啟用LISP的Vlan注入/32 null0主機路由;因此,IGP輔助模式的正確配置是「ip lisp etr」。
# In the IGP support mode, using Configuration-> "ip libr-etr" will lead to the unactivated LISP Vlan/; thus, the correct configuration of the IGP support mode is "ip libet".
Common Configuration on both DC2-Agg1 and DC2-Agg2
feature lisp
vrf context tenant-1
ip lisp etr
lisp instance-id 2
ip lisp locator-vrf default
lisp dynamic-eid VLAN144
database-mapping 172.16.144.0/24 10.10.20.1 priority 50 weight 50 # Note that the IP addresses used in DC2 Agg switches are 10.10.20.1 and 10.10.20.2(Which are Loopbacks Configured on DC2-Agg switches)
database-mapping 172.16.144.0/24 10.10.20.2 priority 50 weight 50
map-notify-group 239.254.254.254
no route-export away-dyn-eid
lisp dynamic-eid VLAN244
database-mapping 172.16.244.0/24 10.10.20.1 priority 50 weight 50
database-mapping 172.16.244.0/24 10.10.20.2 priority 50 weight 50
map-notify-group 239.254.254.254
no route-export away-dyn-eid
vrf context tenant-2
ip lisp etr
lisp instance-id 3
ip lisp locator-vrf default
lisp dynamic-eid VLAN145
database-mapping 172.16.145.0/24 10.10.20.1 priority 50 weight 50
database-mapping 172.16.145.0/24 10.10.20.2 priority 50 weight 50
map-notify-group 239.254.254.254
no route-export away-dyn-eid
Configuration on DC2-Agg1
interface Vlan144
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-1
lisp mobility VLAN144
lisp extended-subnet-mode
ip address 172.16.144.252/24
ip pim sparse-mode
hsrp 144
preempt
priority 254
ip 172.16.144.254
interface Vlan145
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-2
lisp mobility VLAN145
lisp extended-subnet-mode
ip address 172.16.145.252/24
ip pim sparse-mode
hsrp 145
preempt
priority 254
ip 172.16.145.254
interface Vlan244
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-1
lisp mobility VLAN244
lisp extended-subnet-mode
ip redirects
ip address 172.16.244.252/24
hsrp 244
preempt
priority 254
ip 172.16.244.254
interface loopback100
ip address 10.10.20.1/32
ip router eigrp 100
ip pim sparse-mode
Configuration on DC2-Agg2
interface Vlan144
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-1
lisp mobility VLAN144
lisp extended-subnet-mode
ip address 172.16.144.253/24
ip pim sparse-mode
hsrp 144
ip 172.16.144.254
interface Vlan145
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-2
lisp mobility VLAN145
lisp extended-subnet-mode
ip address 172.16.145.253/24
ip pim sparse-mode
hsrp 145
ip 172.16.145.254
interface Vlan244
no shutdown
vrf member tenant-1
lisp mobility VLAN244
lisp extended-subnet-mode
no ip redirects
ip address 172.16.244.253/24
hsrp 244
preempt
ip 172.16.244.254
interface loopback100
ip address 10.10.20.2/32
ip router eigrp 100
ip pim sparse-mode
#DC1和DC2 Agg LISP配置之間的區別是「資料庫對映」中定義的環回。 在DC1配置中,將使用DC1-Agg1和DC1-Agg2的環回來定義資料庫對映;對於DC2,將使用DC2-Agg1和DC2-Agg2中的環回來定義資料庫對映
The difference between the #DC1 and DC2AggLIP configurations is the loops defined in the "Database Collapse". In the DC1 configuration, the loops from DC1-Agg1 and DC1-Agg2 will be used for mapping databases; for DC2 the loops from DC2-Agg1 and DC2-Agg2 will be used for mapping databases from DC2-Agg2.
#下面顯示的其他IGP/路由對映/字首清單配置將相似(為介面分配的IP地址確實不同)
# The other IGP/routing mapping/first list configuration shown below will be similar (the IP address assigned to the interface will be different)
router eigrp 100
address-family ipv4 unicast
vrf tenant-1
distance 90 245 # External EIGRP Routes have to have an AD which is higher than the default LISP AD(which is 240); Reason being, if the redistributed route from dc1-agg1 comes back to dc1-agg2 via eigrp, default EIGRP External is 170 which will override LISP route causing problems
redistribute lisp route-map lisp-to-eigrp # This command is to redistribute LISP /32 routes only to the IGP(EIGRP In this example)
redistribute direct route-map direct # This is needed so that the direct routes(/24 SVI routes in LISP) are redistributed to the IGP; This will be needed if there is some device that is trying to communicate to a silent host in the LISP enabled Vlan
vrf tenant-2
distance 90 245
redistribute lisp route-map lisp-to-eigrp
redistribute direct route-map direct
#啟用LISP的AGG VDC也會與核心端形成IGP鄰居關係
# AGG VDC that activates LISP will also form the IGP Neighborhood & nbsp at the core.
#在本示例中,使用屬於每個租戶VRF的子介面形成面向核心的鄰居關係,如下所示。
# In this example, a child interface belonging to each tenant VRF is used to form a core-oriented neighbourhood relationship, as shown below.
interface Ethernet3/6.111 encapsulation dot1q 111 vrf member tenant-1 ip address 192.168.98.1/30 ip router eigrp 100 no shutdown interface Ethernet3/6.212 encapsulation dot1q 212 vrf member tenant-2 ip address 192.168.198.1/30 ip router eigrp 100 no shutdown
ip prefix-list lisp-to-eigrp seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 ge 32 # This is the prefix list that is matching any /32 routes which are to be redistributed from LISP To IGP route-map direct permit 10 # This is for the Direct routes route-map lisp-to-eigrp deny 10 # This is to prevent any null0 routes from being redistributed to IGP from LISP match interface Null0 route-map lisp-to-eigrp permit 20 # This is to allow redistribution of /32 host routes match ip address prefix-list lisp-to-eigrp
#所有AGG交換機(DC1和DC2)都需要上述所有配置。 請記住,為SVI、環回和HSRP VIP提供唯一的IP地址對於所有SVI都是相同的
#All AGG switches (DC1 and DC2) need all the above configurations. Remember, the only IP addresses available for SVI, Ring and HSRP VIP are the same for all SVIs.
HSRP過濾
HSRP filtered.
#對於IGP輔助部署,當通過OTV或任何其他機制擴展時,必須建立FHRP隔離;
# For IGP deployments, FHRP isolation must be established when expanded through OTV or any other mechanism; & nbsp;
#通過在OTV VDC中過濾FHRP Hello消息來完成此操作
# It's done by filtering FHRP Hello in OTV VDC
#在本示例中,使用了N7k OTV,因此應用了以下配置來過濾OTV VDC中的FHRP資料包。
# In this example, N7k OTV is used, so the following configuration is used to filter the FHRP package in OTV VDC.
ip access-list ALL_IPs
10 permit ip any any
mac access-list ALL_MACs
10 permit any any
ip access-list HSRP_IP
10 permit udp any 224.0.0.2/32 eq 1985
20 permit udp any 224.0.0.102/32 eq 1985
mac access-list HSRP_VMAC
10 permit 0000.0c07.ac00 0000.0000.00ff any
20 permit 0000.0c9f.f000 0000.0000.0fff any
arp access-list HSRP_VMAC_ARP
10 deny ip any mac 0000.0c07.ac00 ffff.ffff.ff00
20 deny ip any mac 0000.0c9f.f000 ffff.ffff.f000
30 permit ip any mac any
vlan access-map HSRP_Localization 10
match mac address HSRP_VMAC
match ip address HSRP_IP
action drop
vlan access-map HSRP_Localization 20
match mac address ALL_MACs
match ip address ALL_IPs
action forward
vlan filter HSRP_Localization vlan-list 144-145
ip arp inspection filter HSRP_VMAC_ARP vlan 144-145
mac-list OTV_HSRP_VMAC_deny seq 10 deny 0000.0c07.ac00 ffff.ffff.ff00
mac-list OTV_HSRP_VMAC_deny seq 11 deny 0000.0c9f.f000 ffff.ffff.f000
mac-list OTV_HSRP_VMAC_deny seq 20 permit 0000.0000.0000 0000.0000.0000
route-map OTV_HSRP_filter permit 10
match mac-list OTV_HSRP_VMAC_deny
otv-isis default
vpn Overlay0
redistribute filter route-map OTV_HSRP_filter
#僅在OTV VDC上需要FHRP過濾配置;如果使用ASR OTV部署,則過濾機制應根據ASR配置指南的相關內容進行使用和記錄。
#FHRP filter configuration is needed only on OTV VDC; if ASR OTV is deployed, filtering should be used and documented according to the contents of the ASR configuration guidelines.
OTV抑制ARP
OTV inhibits ARP
#禁用OTV VDC上的ARP和快取功能
# Disables ARP and Cache on OTV VDC
interface Overlay0 no otv suppress-arp-nd >>>>>
DC1-AGG1# show ip route lisp vrf tenant-1
IP Route Table for VRF "tenant-1"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.0/25, ubest/mbest: 1/0
*via Null0, [240/1], 07:22:30, lisp, dyn-eid
172.16.144.128/25, ubest/mbest: 1/0
*via Null0, [240/1], 07:22:30, lisp, dyn-eid
#當SVI 144上啟用LISP時,將會自動建立兩個Null0路由;SVI 144是/24子網,因此第一條null0路由來自172.16.144.0/25,第二條null0路由來自172.16.144.128/25,如上所述。
# When the LISP is activated on SVI 144, two Null0 routes will be built automatically; SVI 144 is a 24-son network, so the first null0 route is from 172.16.144.0/25 and the second null0 route is from 172.216.144.128/25, as described above. & nbsp;
#這是預期的,也是設計好的;這樣做是為了確保來自未發現主機的資料包觸發RPF異常,這將導致資料包被傳送到CPU,並最終有助於主機檢測(EID)
# This is expected and designed; this is to ensure that an undetected host package triggers RPF anomalies, which will result in the transfer of the data package to the CPU and eventually help with the mainframe inspection (EID)
#啟用LISP的介面上的主機檢測基於從資料庫對映配置中指定的範圍內的IP地址接收L3流量。
#Initiating the host inspection on the LISP interface is based on receiving L3 traffic from an IP address within the range specified in the database mapping configuration.
為了方便檢測主機,請注意,在介面上啟用LISP時:
# RPF異常在介面上啟用,以便由未知源生成的資料包觸發異常
# LISP來源的Null0路由被安裝,以確保未知來源觸發RPF異常
To facilitate the detection of the host, note that when the LISP is activated on the interface:
#RPF is not usually activated on the interface to trigger an anomaly from an unknown source
#LISP source's Null0 route is installed to ensure that an unknown source triggers an anomaly in the RPF
由於此解決方案依賴OTV在兩個資料中心之間進行L2擴展,因此ARP信令不能直接用於檢測IP主機,因為在許多情況下會廣播給所有交換機。
Since the solution relies on an extension of L2 between the two data centres by OTV, the ARP message cannot be used directly to detect IP hosts, as in many cases it will be broadcast to all switchboards.
但是,ARP訊號用作LISP可能存在未檢測到的主機的指示。由於主機可以駐留在OTV網橋的任何一側,LISP在學習新的IP-MAC繫結後啟動本地化機制。
定位機制的工作原理如下:
#交換機獲知新的IP-MAC繫結(通過GARP、RARP或ARP請求)。
#用作活動HSRP的交換機向主機傳送回應要求但源自HSRP VIP地址
#主機對回應請求作出回覆,但在OTV中進行FHRP隔離後,僅在主機所在的DC站點上收到回應回覆
#由於回應應答是L3資料包,因此LISP會檢測到主機。
However, the ARP signal is used as an undetected host's instructions. Since the host can stay on any side of the OTV network, LISP initiates a localization system after learning about the new IP-MAC connection.
locator system works on the following principles:
#The switchboard is aware of the new IP-MAC bond (requested by GARP, RARP or ARP).
# The switch used as activity HSRP to send the request back to the host but originated from the HSRP VIP address
& nbsp; #The host responded to the request but received a reply from FHRP partition in OTV only on the host's DC site
& nbsp;# Since the response was a L3 data package, LISP will check the host.
#如果在任何啟用了LISP的SVI上收到IP資料包,則該資料包自身將向LISP進程傳送通知,通知該端點為本地;將不會傳送任何ICMP ECHO要求以進一步確認主機是否為本地主機。因此,必須注意的是,從DC2主機到DC1-AGG SVI IP地址執行Ping操作會導致終端標識損壞,這也會導致ping丟失或流量黑洞,因為主機現在被標識為DC1中的本地EID,而不是DC2。因此,Ping操作不應從LISP環境中的SVI IP地址發出,因為這可能損壞路由表並導致流量黑洞。如果啟用LISP的Vlan中的主機嘗試對SVI IP地址執行ping,也會發生相同的問題;對VIP執行ping操作應該沒問題,因為兩端都存在且處於活動狀態,而站點本地將捕獲資料包。
# If an IP package is received on any SIVI that activates LISP, the package itself will send a notification to LISP that the endpoint is local; it will not send any ICMP ECHO that requires further confirmation that the host is a local host. It must therefore be noted that Ping from the DC2 host to the DC1-AGSVI IP address will cause a final sign loss, which will cause a ping loss or a traffic black hole, as the host is now identified as the local ED in DC1 instead of DC2. Therefore, Ping should not be sent from the SVI IP address in the LISP environment, because it may damage the path by a watch and lead to a black hole. If the host in the Vlan that activates LISP is trying to apply the SVI IP address, there will be a similar problem; there should be no problem with implementing the VIP.
以下是DC1中主機聯機時的路由表條目示例:
The following is an example of the route line of the DC1 host network:
DC1-AGG1# show ip route 172.16.144.1 vrf tenant-1
IP Route Table for VRF "tenant-1"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.1/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached
*via 172.16.144.1, Vlan144, [240/1], 3d05h, lisp, dyn-eid
via 172.16.144.1, Vlan144, [250/0], 3d05h, am
DC1-AGG2# sh ip route 172.16.144.1 vr tenant-1
IP Route Table for VRF "tenant-1"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.1/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached
*via 172.16.144.1, Vlan144, [240/1], 3d05h, lisp, dyn-eid
via 172.16.144.1, Vlan144, [250/0], 3d05h, am
#如上所示,有兩條路由;一個通過LISP進程,管理距離為240,另一個通過AM->鄰接管理器(由ARP進程填充),其AD為250。
# As indicated above, there are two routes; one through LISP, managing a distance of 240, and the other through AM-> and the Neighbor Manager (filled by ARP) with AD 250.
#DC1中的兩台Agg交換機將具有相同的條目。
Two Agg switches in DC1 will have the same entry.
#此外,LISP將在動態EID表中列出主機的相同條目,如下所示。
# In addition, LISP will list the same entry as the host in the dynamic EID table as shown below.
DC1-AGG1# show lisp dynamic-eid detail vrf tenant-1 | in 144.1, nex 1
172.16.144.1, Vlan144, uptime: 3d05h, last activity: 00:14:38
Discovered by: packet reception
DC1-AGG2# show lisp dynamic-eid detail vrf tenant-1 | in 144.1, nex 1
172.16.144.1, Vlan144, uptime: 3d05h, last activity: 00:00:37
Discovered by: site-based Map-Notify
#發現這兩種情況都不同;HSRP活動的DC1-AGG1通過「資料包接收」方式記錄條目,這基本上意味著有一個資料包傳入並新增為EID
# It turns out they're both different; DC1-AGG1 of HSRP activity records entries via "data packs" which basically means that a data package is sent in and added to EID
#一旦Agg1得知某個EID,它就從源IP-> Loopback100 IP地址(在資料庫對映下定義)向組 — > 239.254.254.254(配置如上所述)傳送組播消息,vPC對等交換機也會收到該消息,並相應地填充該條目,由於資料庫對映具有dc1-agg1和dc1-agg2的IP地址,因此該條目被視為本地EID。該組播資料包也將通過OTV到達遠端站點;但是,遠端站點會檢查資料庫對映,並且由於此資料包來自與「資料庫對映」不同的IP地址,因此DC2 AGg交換機不會將其視為本地EID。
# Once Agg1 becomes aware of an EID, it sends a message from the source IP-> Loopback 100 IP address (defined in a database mapping) to the group - > 239 254.254.254 (configuration as described above), the VPC swapper will also receive it and fill it appropriately, and the IP address dc1-agg1 and dc1-agg2 will be shown in the database, so the item will be considered as the local ED. The package will also go through OTV to the remote site; however, the remote site site will check the mapping of the database and is derived from an IP address that is different from the `database mapping', so the DC2 AG switcher will not view it as the local ED.
#當啟用LISP的SVI檢測到主機時,觸發的「map-notify」消息將傳送到相應動態EID配置下定義的組播組
# When the host is detected using LISP's SVI, the triggering "map-notify" message will be sent to the group defined by the reaction ED configuration
#除了觸發的對映通知消息外,該vlan中的HSRP Active(或FHRP active)交換機還會定期傳送對映通知消息;
# In addition to the trigger alert, the HSRP Active (or FHRP Active) switch in the vlan regularly sends notification messages; & nbsp;
#對映通知消息的PCAP如下所示。
#PAP for the mapping of the notification message is shown below.
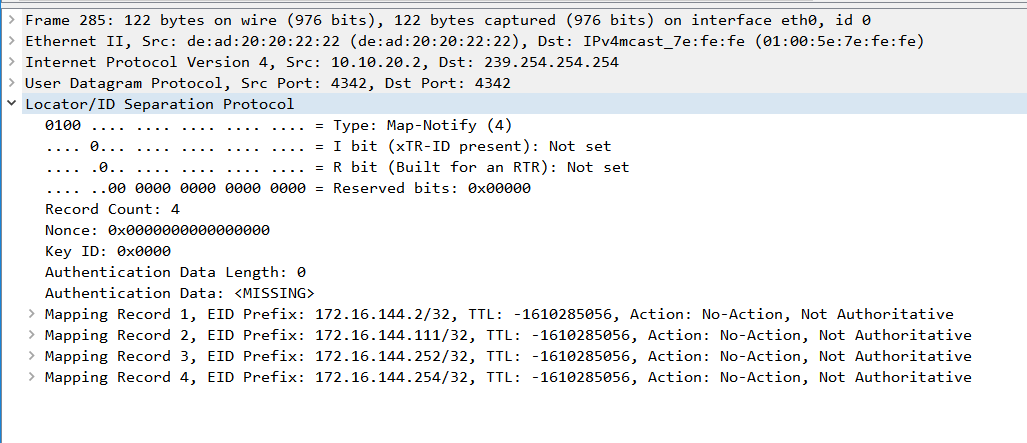
#這是IGP協助模式的關鍵;任何/32 LISP路由都將重新分發到IGP;這可以通過在EIGRP下應用的「redistribute LISP」命令實現。
# This is the key to the IGP help model; any /32 LISP route will be redistributed to IGP; this can be done through the "redistribute LISP" command applied under EIGRP. & nbsp; & nbsp;
#重新分發後,任何/32主機路由都會被視為EIGRP外部路由。為了提高EIGRP管理距離,已對其進行調整。這是為了確保LISP路由停留在URIB中,而不是傳入的EIGRP外部路由。如;DC1-Agg1和DC1-Agg2是具有DC1-core的EIGRP鄰居。DC1-AGG1通過重分發將/32路由注入到DC1-Core。既然DC1-Core是DC1-Agg2的EIGRP鄰居,那麼相同的路由可能返回DC1-Agg2,如果EIGRP AD為170,則有機會贏取LISP路由(其AD為240);因此,為了避免這種情況,EIGRP外部路由AD已修改為245。
# #32 host roads are treated as EIGRP external routes after re-distribution. To improve EIGRP management distance, adjustments have been made. This is to ensure that the LISP route stays in the URB, rather than the EIGRP external route that is passed on. e.g. DC1-Agg1 and DC1-Agg2 are neighbours of EIGRP with DC1-core. DC1-AG1 injects 32 by re-distribution to DC1-Core. Since DC1-Core is a neighbor of DC1-Agg2, the same route may return to DC1-Agg2, and if EIGRP AD is 170, there is an opportunity to win the LISRP route (AD 240); thus, in order to avoid this situation, the EIGRP external route has been modified by AD to 245;
#由DC1-Agg交換機獲知的/32路由被重新分發到EIGRP,而DC1-core條目如下所示。
#32 route known by the DC1-Agg switchboard was redistributed to EIGRP, while the DC1-core entry is as follows. & nbsp;
DC1-CORE# sh ip route 172.16.144.1
IP Route Table for VRF "default"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.1/32, ubest/mbest: 2/0
*via 192.168.98.1, Eth3/20.111, [170/51456], 00:00:01, eigrp-100, external
*via 192.168.98.5, Eth3/22.112, [170/51456], 18:14:51, eigrp-100, external
#該路由存在於全域性路由表中,並且在核心端未配置VRF。
# The route is in the global route table and VRF is not configured at the core. & nbsp;
#由於在AGG交換機上配置了「redistribute direct」,核心層還將為父子網提供/24 ECMP路由,如下所示。這將有助於為無提示主機(沒有/32路由)吸引流量。
# As a result of the configuration of the AGG switchboard "redistribute direct" the core layer will also provide a parent/child network with a route /24 ECMP, as shown below. This will help to attract traffic for the unattended host (no 32 route).
DC1-CORE# sh ip route 172.16.144.10 # Checking for a non existent Host 172.16.144.10
IP Route Table for VRF "default"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.0/24, ubest/mbest: 2/0
*via 192.168.98.1, Eth3/20.111, [170/51456], 00:02:13, eigrp-100, external
*via 192.168.98.5, Eth3/22.112, [170/51456], 18:17:03, eigrp-100, external
#此外,DC1和DC2核心都可看到/24 ECMP路由
# In addition, the DC1 and DC2 cores can see 24 ECMP routes
Branch1-Router# sh ip route 172.16.144.10
Routing entry for 172.16.144.0/24
Known via "eigrp 100", distance 170, metric 51712, type external
Redistributing via eigrp 100
Last update from 192.168.99.2 on GigabitEthernet0/0/1, 00:00:17 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
192.168.99.2, from 192.168.99.2, 00:00:17 ago, via GigabitEthernet0/0/1 # 192.168.99.2 is DC2-Core
Route metric is 51712, traffic share count is 1
Total delay is 1020 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is 100000 Kbit
Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1492 bytes
Loading 1/255, Hops 2
* 192.168.99.1, from 192.168.99.1, 00:00:17 ago, via GigabitEthernet0/0/1 # 192.168.99.1 is DC1-Core
Route metric is 51712, traffic share count is 1
Total delay is 1020 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is 100000 Kbit
Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1492 bytes
Loading 1/255, Hops 2
#此路由可確保分支主機可以到達位於任一位置的靜默主機。
# This route ensures that the branch hosts can reach a silent host at any location. #nbsp
#當DC1-Host1 -> 172.16.144.1嘗試到達DC2-Host1-> 172.16.144.2時,這是VLAN內資料中心間流量。DC1-Host 1發出一個ARP請求,該請求將一直穿過OTV並到達DC2-Host1
# When DC1-Host1-> 172.16.144.1 tries to reach DC2-Host1-> 172.16.144.2, this is the central flow of data in VLAN. DC1-Host 1 sends an ARP request that will pass through the OTV and reach DC2-Host1
# DC2-Host1使用返回到DC1-Host1的ARP應答進行響應
# DC2-Host1 responded with an ARP response returned to DC1-Host1
#後續ICMP資料包通過OTV傳送
# And after ICMP's package is sent through OTV
#當DC1-Host1-> 172.16.144.1嘗試到達DC2-Host2-> 172.16.244.2時,資料包不會在DC1中從VLAN 144路由到244;相反,它遵循從DC1-Agg到DC1-Core的路由路徑,然後到達DC2-Core,最終路由將由DC2-Agg交換機完成到目標Vlan-244的路由。
# When DC1-Host1-> 172.16.144.1 tries to reach DC2-Host2-> 172.16.244.2, the package will not travel from VLAN 144 to 244 in DC1; instead, it follows the route from DC1-Agg to DC1-Core, then to DC2-Core, where the final route will be completed by the DC2-Agg switchboard to target Vlan-244.
#從DC1-Host1到DC2-Host2的traceroute如下所示。
# Traceroute from DC1-Host1 to DC2-Host2 as shown below.
DC1-HOST# traceroute 172.16.244.2 vrf vlan144 traceroute to 172.16.244.2 (172.16.244.2), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 172.16.144.250 (172.16.144.250) 1.149 ms 0.841 ms 0.866 ms # DC1-AGG1 2 192.168.98.2 (192.168.98.2) 1.004 ms 0.67 ms 0.669 ms # DC1-CORE 3 192.168.99.2 (192.168.99.2) 0.756 ms 0.727 ms 0.714 ms # DC2-CORE 4 192.168.94.5 (192.168.94.5) 1.041 ms 0.937 ms 192.168.94.1 (192.168.94.1) 1.144 ms # DC2-Agg1/DC2-Agg2 5 172.16.244.2 (172.16.244.2) 2.314 ms * 2.046 ms # DC2-Host2
#這將遵循與一個VLAN到另一個VLAN的VLAN間DC通訊相同的方式(上一個示例)
# This will follow the same way one VLAN communicates to another VLAN VLAN DC (the previous example)
#當DC1-host1-> 172.16.144.1嘗試到達DC2-Host3-> 172.16.145.2時,這是源自Vlan 144(VRF租戶–1)且目的地為Vlan 145(VRF租戶–2)的DC間流量。 與常規N7k OTV部署不同,此流量的處理方式略有不同。DC1端不會發生任何vlan間路由;相反,此流量將被路由並傳送到DC1-core,核心層會進一步通過IGP路由到DC2-Core
# When DC1-host1-> 172.144.1 tries to reach DC2-Host3-> 172.16.145.2, this is a DC-to-DC flow from Vlan 144 (VRF-1) and destined for Vlan 145 (VRF-2). Unlike normal N7k OTV deployments, this flow is handled slightly differently. There will be no vlan route at the DC1 end; on the contrary, the flow will be routed to DC1-core, and the core layer will move further from DC2-Core through the IGP route.
#在本檔案中,VRF間洩漏是由核心交換機在每個站點完成的。可以是任何裝置(如防火牆);如果VRF間洩漏存在,則從LISP配置的角度不會有任何更改。
# In this file, VRF leaks are performed by a core switch at each site. It can be any device (e.g. firewalls); if VRF leaks exist, there will be no change from the LISP configuration. & nbsp;
DC1-AGG1# sh ip route 172.16.145.2 vrf tenant-1
IP Route Table for VRF "tenant-1"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.145.2/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0
*via 192.168.98.2, Eth3/6.111, [245/51968], 00:00:46, eigrp-100, external
#從DC1-Host1到DC2-Host3的Traceroute將同樣顯示其not-inter-vlan路由,而不是第3層通過核心路由。簡而言之,VLAN間流量將不會使用OTV。
# Traceroute from DC1-Host1 to DC2-Host3 will also show its not-inter-vlan route, rather than the third level through the core route. In short, VLAN traffic will not use the OTV.
DC1-HOST# traceroute 172.16.145.2 vrf vlan144 traceroute to 172.16.145.2 (172.16.145.2), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets 1 172.16.144.250 (172.16.144.250) 1.049 ms 0.811 ms 0.81 ms # DC1-AGG1 2 192.168.98.2 (192.168.98.2) 0.844 ms 0.692 ms 0.686 ms # DC1-CORE 3 192.168.99.2 (192.168.99.2) 0.814 ms 0.712 ms 0.735 ms # DC2-CORE 4 192.168.194.1 (192.168.194.1) 0.893 ms 0.759 ms 192.168.194.5 (192.168.194.5) 0.89 ms # DC2-Agg1/DC2-Agg2 5 172.16.145.2 (172.16.145.2) 1.288 ms * 1.98 ms # DC2-Host3 DC1-HOST#
# Branch-1-172.17.200.1中的主機嘗試到達DC2-Silent Host- 172.16.144.119。由於主機處於靜默狀態,因此DC2中將不存在任何/32路由。
# The host in Branch-1-172.1.7.200.1 tried to reach DC2-Silent Host-17.16.144.119. As the host is in a state of silence, there will be no /32 route in DC2. & nbsp;
DC2-AGG1# show ip route 172.16.144.119 vr tenant-1
IP Route Table for VRF "tenant-1"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.0/25, ubest/mbest: 1/0
*via Null0, [240/1], 20:48:29, lisp, dyn-eid
DC2-AGG2# show ip route 172.16.144.119 vr tenant-1
IP Route Table for VRF "tenant-1"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.0/25, ubest/mbest: 1/0
*via Null0, [240/1], 20:48:13, lisp, dyn-eid
#根據LISP設計,路由172.16.144.119將匹配到172.16.144.0/25 null0路由。
# Route 172.16.144.119 will match 172.16.144.0/25 null0 route according to LISP design. & nbsp;
#當Branch路由器收到目的IP為172.16.144.119的資料包時,URIB具有到DC1-core和DC2-core的ECMP /24路由。這基本上意味著該資料包將傳送到核心層交換機之一。
# When the Branch router receives the data package IP 172.16.144.119, the URIB has the ECMP/24 route to DC1-core and DC2-core. This basically means that the data package will be sent to one of the core layers.
Branch1-Router# sh ip route 172.16.144.119
Routing entry for 172.16.144.0/24
Known via "eigrp 100", distance 170, metric 51712, type external
Redistributing via eigrp 100
Last update from 192.168.99.2 on GigabitEthernet0/0/1, 00:08:54 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
192.168.99.2, from 192.168.99.2, 00:08:54 ago, via GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Route metric is 51712, traffic share count is 1
Total delay is 1020 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is 100000 Kbit
Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1492 bytes
Loading 1/255, Hops 2
* 192.168.99.1, from 192.168.99.1, 00:08:54 ago, via GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Route metric is 51712, traffic share count is 1
Total delay is 1020 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is 100000 Kbit
Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1492 bytes
Loading 1/255, Hops 2
Branch1-Router#sh ip cef exact-route 172.17.200.1 172.16.144.119 dest-port 1
172.17.200.1 -> 172.16.144.119=>IP adj out of GigabitEthernet0/0/1, addr 192.168.99.1
#根據CEF的資料包正在雜湊到192.168.99.1(即DC1-Core)
# According to the CEF's data pack is amassing 192.168.99.1 (i.e. DC1-Core)
# DC1-Core有2個ECMP路徑;一個指向DC1-Agg1(HSRP活動),另一個指向DC1-Agg2(HSRP備用)。 在路由雜湊中,所選路徑將是DC1-Agg2。
# DC1-Core has two ECMP paths; one to DC1-Agg1 (HSRP activity) and the other to DC1-Agg2 (HSRP back-up) The path selected will be DC1-Agg2.
DC1-CORE# sh routing hash 172.17.200.1 172.16.144.119 1 1
Load-share parameters used for software forwarding:
load-share mode: address source-destination port source-destination
Universal-id seed: 0xfdba3ebe
Hash for VRF "default"
Hash Type is 1
Hashing to path *192.168.98.5 Eth3/22.112
For route:
172.16.144.0/24, ubest/mbest: 2/0
*via 192.168.98.1, Eth3/20.111, [170/51456], 00:19:57, eigrp-100, external
*via 192.168.98.5, Eth3/22.112, [170/51456], 18:34:47, eigrp-100, external
DC1-CORE# sh cdp nei int e3/22
Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge
S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater,
V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device,
s - Supports-STP-Dispute
Device-ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID
DC1-AGG2(JAF1534CHCJ)
Eth3/22 172 R S s N7K-C7009 Eth3/7
#由於DC1-Agg2在URIB中沒有任何條目,因此將收集資料包並將其傳送到CPU,這將迫使DC1-Agg2從SVI IP地址生成ARP請求,如下所示。
# Since DC1-Agg2 has no item in the URB, the collection of the data package and its transmission to the CPU will force DC1-Agg2 to generate the ARP request from the SVI IP address, as shown below.
2020-02-18 15:09:05.673165 172.17.200.1 -> 172.16.144.119 ICMP 114 Echo (ping) request id=0x0022, seq=0/0, ttl=254
2020-02-18 15:09:05.675041 de:ad:20:19:22:22 -> Broadcast ARP 60 Who has 172.16.144.119? Tell 172.16.144.251
#此ARP請求是一個廣播,它通過OTV擴展在包括DC2的整個第2層域中傳播。
This ARP request is a radio broadcast that is broadcast through the OTV Extension throughout the 2nd floor, including DC2. & nbsp;
# DC2-Silent主機現在響應來自DC1-Agg2的ARP請求
# DC2-Silent hosts now respond to ARP requests from DC1-Agg2
# DC1-Agg2收到來自靜默主機的此ARP應答
# DC1-Agg2 received an ARP response from the silent host
2020-02-18 15:09:05.675797 64:12:25:97:46:41 -> de:ad:20:19:22:22 ARP 60 172.16.144.119 is at 64:12:25:97:46:41
#當收到的資料包是ARP(作為LISP的提示)時,會生成從HSRP VIP-> 172.16.144.254發源併發往靜默主機 — > 172.16.144.119的ICMP ECHO請求。從HSRP VIP發源資料包的意圖是瞭解主機是本地還是遠端。如果主機是遠端主機,則遠端資料中心中也存在FHRP Active,它將捕獲來自主機的ICMP ECHO應答資料包,因此這會導致DC2-Agg2(即HSRP Active)獲知此條目,並且LISP進程現在將基於此IP資料包進行EID Learn。最初來源為來自HSRP VIP的ICMP ECHO請求的DC1-Agg2永遠不會收到響應,因此在DC1端永遠不會進行終端學習;而是DC2端。
# When the package is received from the ARP (as a tip from LISP), it generates an IHRP Active in the remote data centre, which will capture the ICMP ECHO from the Autonomous Machine, which will respond to the data package, so that DC2-Agg2 (i.e., HSRP Active) will be informed of the article and the LISP process will now be based on this IP package EID Learn. The DC1-Agg2 requested by the ICMP ECHO from HSRP VIP will never be heard, and therefore will never be studied at the end of the DC1 end of the DC1 end; & nbsp;
DC2-AGG2# show lisp dynamic-eid detail vrf tenant-1
LISP Dynamic EID Information for VRF "tenant-1"
Dynamic-EID name: VLAN144
Database-mapping [2] EID-prefix: 172.16.144.0/24, LSBs: 0x00000003
Locator: 10.10.20.1, priority: 50, weight: 50
Uptime: 21:50:32, state: up
Locator: 10.10.20.2, priority: 50, weight: 50
Uptime: 21:50:13, state: up, local
Registering more-specific dynamic-EIDs
Registering routes: disabled
Allowed-list filter: none applied
Map-Server(s): none configured, use global Map-Server
Site-based multicast Map-Notify group: 239.254.254.254
Extended Subnet Mode configured on 1 interfaces
Number of roaming dynamic-EIDs discovered: 3
Last dynamic-EID discovered: 172.16.144.254, 00:01:10 ago
Roaming dynamic-EIDs:
172.16.144.2, Vlan144, uptime: 19:09:07, last activity: 00:05:21
Discovered by: packet reception
172.16.144.119, Vlan144, uptime: 00:05:55, last activity: 00:05:55 Discovered by: packet reception
172.16.144.252, Vlan144, uptime: 3d21h, last activity: 00:01:10
Discovered by: packet reception
Secure-handoff pending for sources: none
#一旦LISP進程知道DC2-Agg2(HSRP活動)上的EID,它將
# Once the LISP progresses to the EID on DC2-Agg2 (HSRP) it will
a)本地安裝/32
& nbsp;a) Local installation 32
b)將路由重新分發到DC2-Core
& nbsp;b) Redistribute route to DC2-Core
c)在Vlan中作為組播消息傳送基於站點的通知(在本示例中,消息將發往組 — > 239.254.254.254)
& nbsp;c) Send a message based on a site in Vlan (in this example, the message will be sent to the group - & gt; 239.254.254.254)
DC2-AGG1# show lisp dynamic-eid detail vrf tenant-1
LISP Dynamic EID Information for VRF "tenant-1"
Dynamic-EID name: VLAN144
Database-mapping [2] EID-prefix: 172.16.144.0/24, LSBs: 0x00000003
Locator: 10.10.20.1, priority: 50, weight: 50
Uptime: 21:52:39, state: up, local
Locator: 10.10.20.2, priority: 50, weight: 50
Uptime: 21:52:08, state: up
Registering more-specific dynamic-EIDs
Registering routes: disabled
Allowed-list filter: none applied
Map-Server(s): none configured, use global Map-Server
Site-based multicast Map-Notify group: 239.254.254.254
Extended Subnet Mode configured on 1 interfaces
Number of roaming dynamic-EIDs discovered: 4
Last dynamic-EID discovered: 172.16.144.254, 00:03:07 ago
Roaming dynamic-EIDs:
172.16.144.2, Vlan144, uptime: 19:11:04, last activity: 00:00:21
Discovered by: site-based Map-Notify
172.16.144.110, Vlan144, uptime: 20:04:09, last activity: 20:04:09
Discovered by: site-based Map-Notify
172.16.144.119, Vlan144, uptime: 00:07:52, last activity: 00:00:21 Discovered by: site-based Map-Notify
172.16.144.252, Vlan144, uptime: 21:50:51, last activity: 00:00:21
Discovered by: site-based Map-Notify
Secure-handoff pending for sources: none
#最後,Branch-router1將接收到此/32路由,這將導致Branch路由器將流量傳送到正確的DC2核心交換機。
# Finally, Branch-router1 will receive this /32 route, which will lead Branch routers to send traffic to the right DC2 core switch.
Branch1-Router# sh ip route 172.16.144.119
Routing entry for 172.16.144.119/32
Known via "eigrp 100", distance 170, metric 51712, type external
Redistributing via eigrp 100
Last update from 192.168.99.2 on GigabitEthernet0/0/1, 00:06:25 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.99.2, from 192.168.99.2, 00:06:25 ago, via GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Route metric is 51712, traffic share count is 1
Total delay is 1020 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is 100000 Kbit
Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1492 bytes
Loading 1/255, Hops 2
#考慮到在此拓撲上配置了L2擴展,主機可以從DC1移動到DC2。
# The host can move from DC1 to DC2 taking into account the configuration of the L2 expanse on the pedestal.
#主機 — > 172.16.144.100最初位於Vlan 144和DC1中。
# Host - & gt; 172.16.144.100 originally in Vlan 144 and DC1. & nbsp;
#當主機在DC1中聯機時,DC1-Agg1和DC1-Agg2交換機內的路由將如下所示
# The route inside the DC1-Agg1 and DC1-Agg2 switches when the host is in DC1 will be as follows:
DC1-AGG1# sh ip route 172.16.144.100 vrf tenant-1
IP Route Table for VRF "tenant-1"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.100/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached
*via 172.16.144.100, Vlan144, [240/1], 00:05:03, lisp, dyn-eid
via 172.16.144.100, Vlan144, [250/0], 00:05:05, am
DC1-AGG2# sh ip route 172.16.144.100 vrf tenant-1
IP Route Table for VRF "tenant-1"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.100/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached
*via 172.16.144.100, Vlan144, [240/1], 00:08:05, lisp, dyn-eid
via 172.16.144.100, Vlan144, [250/0], 00:08:07, am
#分支路由器的路由指向DC1-Core(如下所示),而traceroute將指向DC1核心/agg交換機以到達DC1中的主機
The router for the branch router
Branch1-Router#sh ip route 172.16.144.100
Routing entry for 172.16.144.100/32
Known via "eigrp 100", distance 170, metric 51712, type external
Redistributing via eigrp 100
Last update from 192.168.99.1 on GigabitEthernet0/0/1, 00:00:06 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.99.1, from 192.168.99.1, 00:00:06 ago, via GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Route metric is 51712, traffic share count is 1
Total delay is 1020 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is 100000 Kbit
Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1492 bytes
Loading 1/255, Hops 2
Branch1-Router#traceroute 172.16.144.100 source 172.17.200.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 172.16.144.100
VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id)
1 192.168.99.1 1 msec 1 msec 0 msec # DC1-Core
2 192.168.98.5 1 msec 1 msec # DC1-Agg2
192.168.98.1 1 msec # DC1-Agg1
3 172.16.144.100 1 msec 0 msec 1 msec # DC1-Host
#當主機移動到DC2時,它會在Vlan 144中傳送GARP。這在DC2-Agg交換機上可見
# When the host moves to DC2, it sends GRP in Vlan 144. This is available on the DC2-Agg switch.
2020-02-24 22:23:05.024902 Cisco_5a:4a:e7 -> Broadcast ARP 60 Gratuitous ARP for 172.16.144.100 (Request)
#一旦收到帶有ARP/GARP/RARP的資料包,就會觸發本地化機制,向源自VIP的主機發出一個ICMP回應請求
# Once a package with ARP/GARP/RARP is received, a localised scheme is triggered and an ICMP response is sent to the VIP-origin host
2020-02-24 22:23:05.026781 172.16.144.254 -> 172.16.144.100 ICMP 60 Echo (ping) request id=0xac10, seq=0/0, ttl=128
# Host-172.16.144.100現在將響應HSRP VIP
# Host-172.16.144.100 will now respond to HSRP VIP
2020-02-24 22:23:07.035292 172.16.144.100 -> 172.16.144.254 ICMP 60 Echo (ping) reply id=0xac10, seq=0/0, ttl=255
#一旦在DC2-Agg1收到IP資料包,就會導致LISP檢測EID,並在主機路由表中建立一個條目,並開始向EIGRP重分發過程
# Once an IP package is received at DC2-Agg1, it leads to LISP testing EID and creating a block in the host route table and starting to redistribute to EIGRP
DC2-AGG1# sh ip route 172.16.144.100 vrf tenant-1
IP Route Table for VRF "tenant-1"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.100/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0, attached
*via 172.16.144.100, Vlan144, [240/1], 00:00:30, lisp, dyn-eid
via 172.16.144.100, Vlan144, [250/0], 00:00:32, am
#在重分發到位後,DC1-agg站點(此主機的原始所有者)現在會看到RIB中指向EIGRP的更改
# When redistributed, the DC1-agg site (the original owner of this host) will now see changes in the RIB point to EIGRP
DC1-AGG1# sh ip route 172.16.144.100 vrf tenant-1
IP Route Table for VRF "tenant-1"
'*' denotes best ucast next-hop
'**' denotes best mcast next-hop
'[x/y]' denotes [preference/metric]
'%<string>' in via output denotes VRF <string>
172.16.144.100/32, ubest/mbest: 1/0
*via 192.168.98.2, Eth3/6.111, [245/51968], 00:03:47, eigrp-100, external
#遠端分支路由器現在將看到路由更改,traceroute將反映DC2核心/Agg交換機的路徑更改,如下所示
# The remote branch router will now see a change of route and traderoute will reflect a change of path for the DC2 core/Agg switch, as shown below
Branch1-Router#sh ip route 172.16.144.100
Routing entry for 172.16.144.100/32
Known via "eigrp 100", distance 170, metric 51712, type external
Redistributing via eigrp 100
Last update from 192.168.99.2 on GigabitEthernet0/0/1, 00:00:00 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.99.2, from 192.168.99.2, 00:00:00 ago, via GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Route metric is 51712, traffic share count is 1
Total delay is 1020 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is 100000 Kbit
Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1492 bytes
Loading 1/255, Hops 2
Branch1-Router#traceroute 172.16.144.100 source 172.17.200.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 172.16.144.100
VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id)
1 192.168.99.2 1 msec 0 msec 1 msec # DC2-Core
2 192.168.94.1 1 msec 1 msec 1 msec # DC2-Agg1
3 172.16.144.100 0 msec 0 msec 1 msec # Host-after move to DC2
# show lisp dynamic-eid detail vrf <VRF Name>
# Show ip route lisp vrf <VRF Name>
# show lisp dynamic-eid summary vrf <VRF Name>
注册有任何问题请添加 微信:MVIP619 拉你进入群

打开微信扫一扫
添加客服
进入交流群



















发表评论